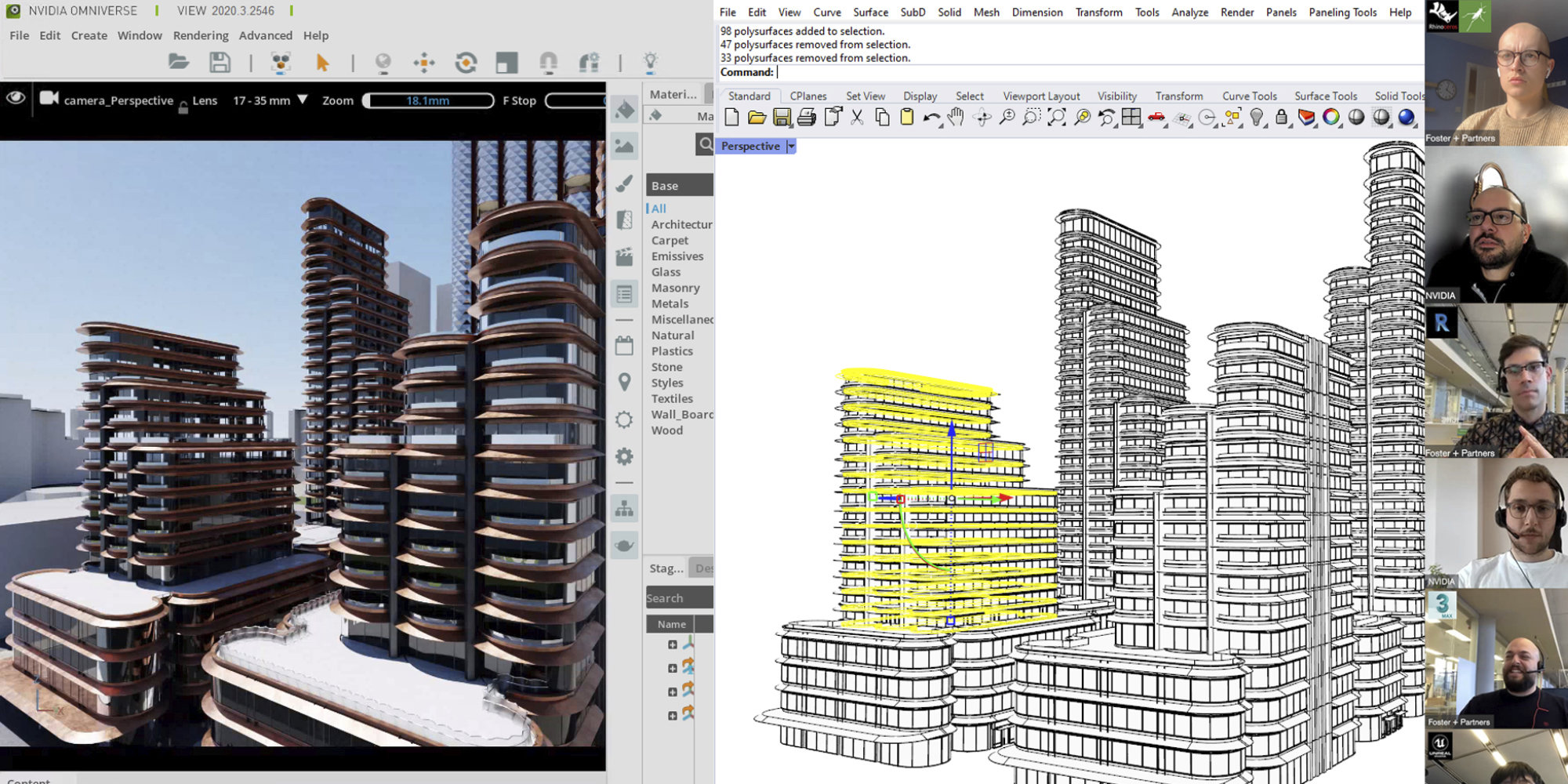
The Applied R+D team (Applied Research + Development) is an integrated multi-disciplinary team of architects and engineers, who are also expert programmers. Our expertise ranges from art, architecture, and computer science to landscape architecture, structural engineering and applied mathematics.
Applied R+D
We conduct state-of-the-art research and development to solve complex design challenges, taking the latest advances out of the lab and into the hands of architects and engineers. We have specific expertise in computational design, performance analysis, optimisation, fabrication and interaction design, and we work with new technologies such as augmented reality, machine learning, and real-time simulation. This underpins the practice’s integrated approach, where architects and engineers can combine the best of human intuition with computational rigour.
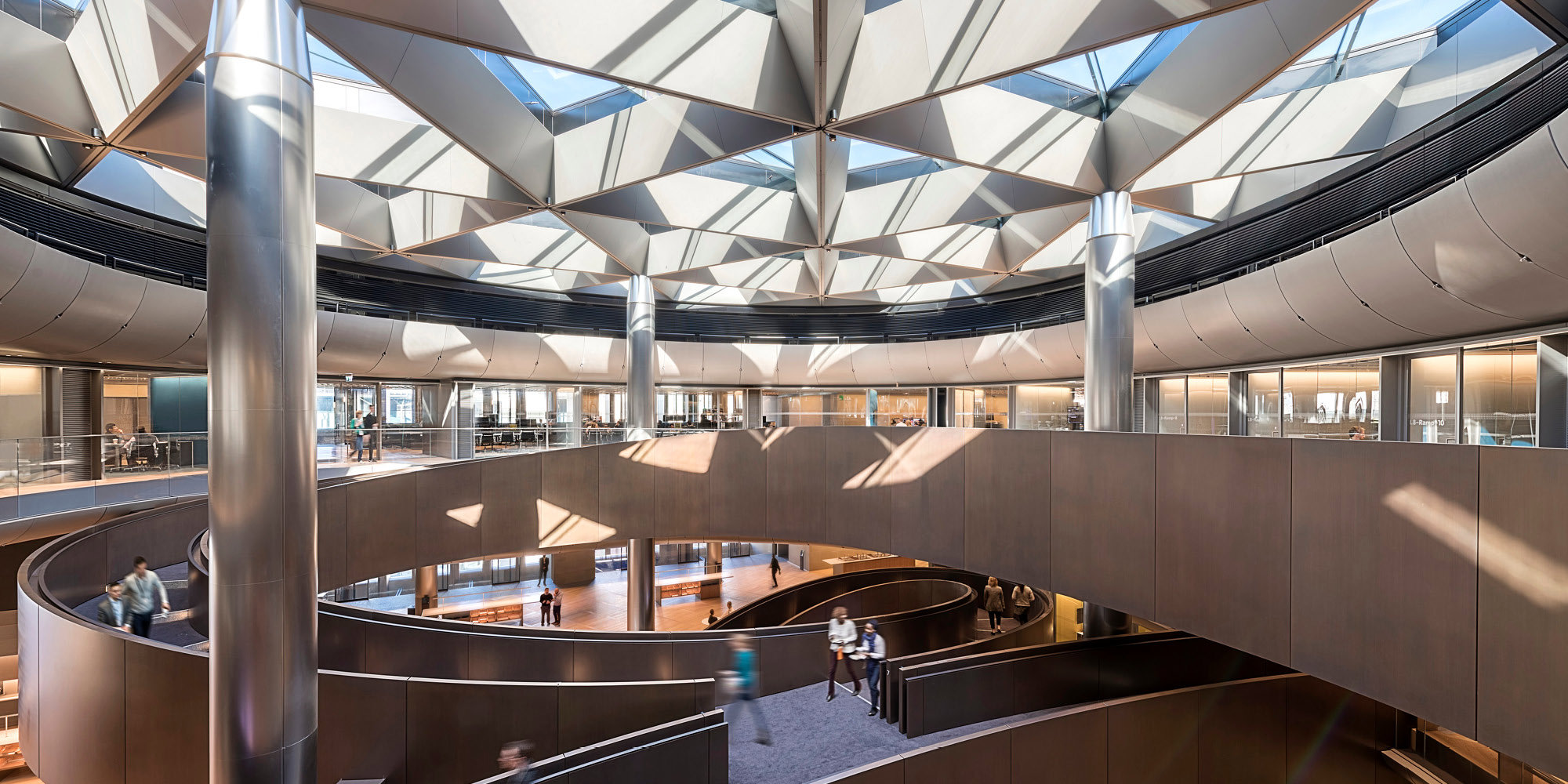
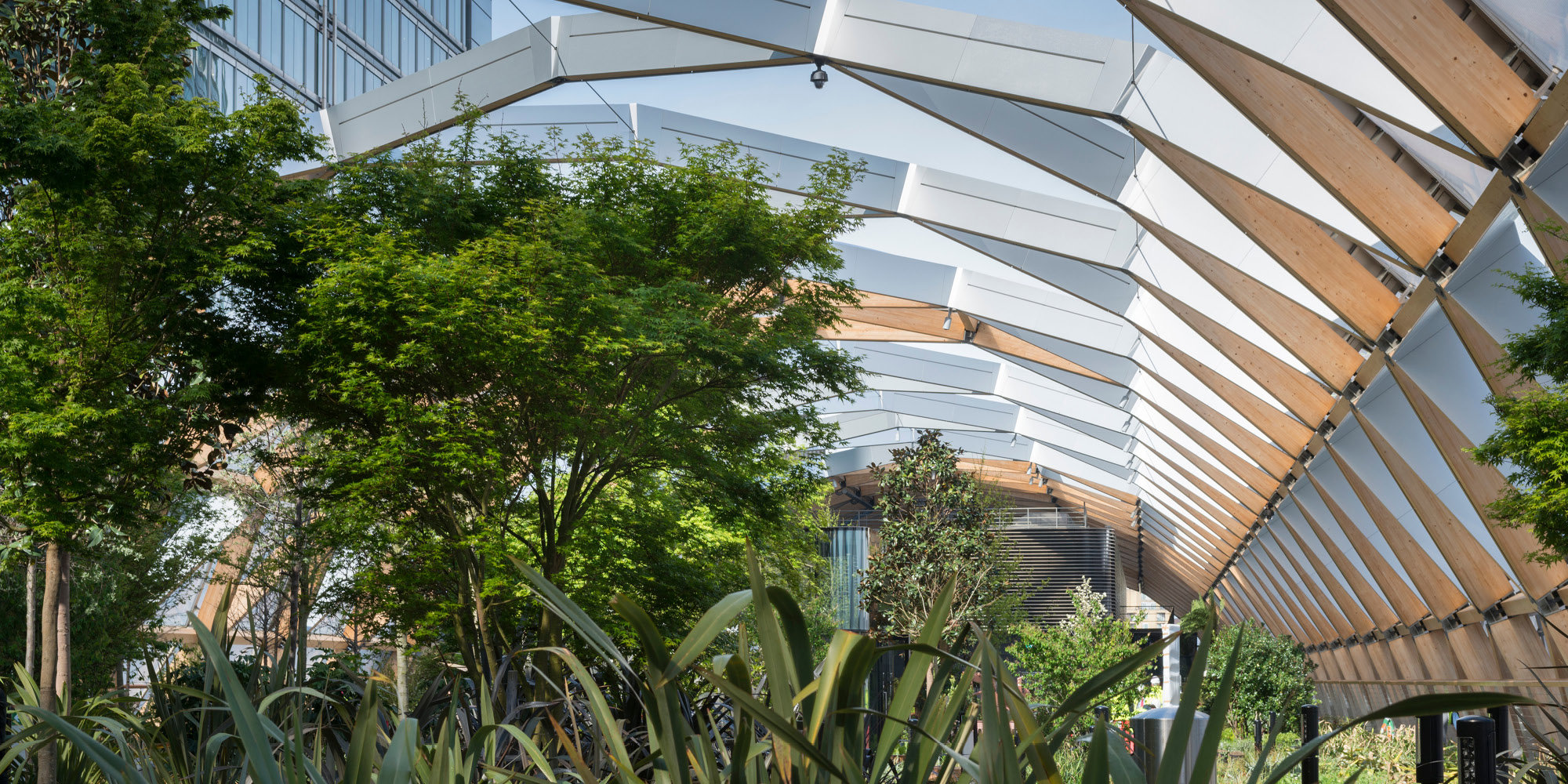
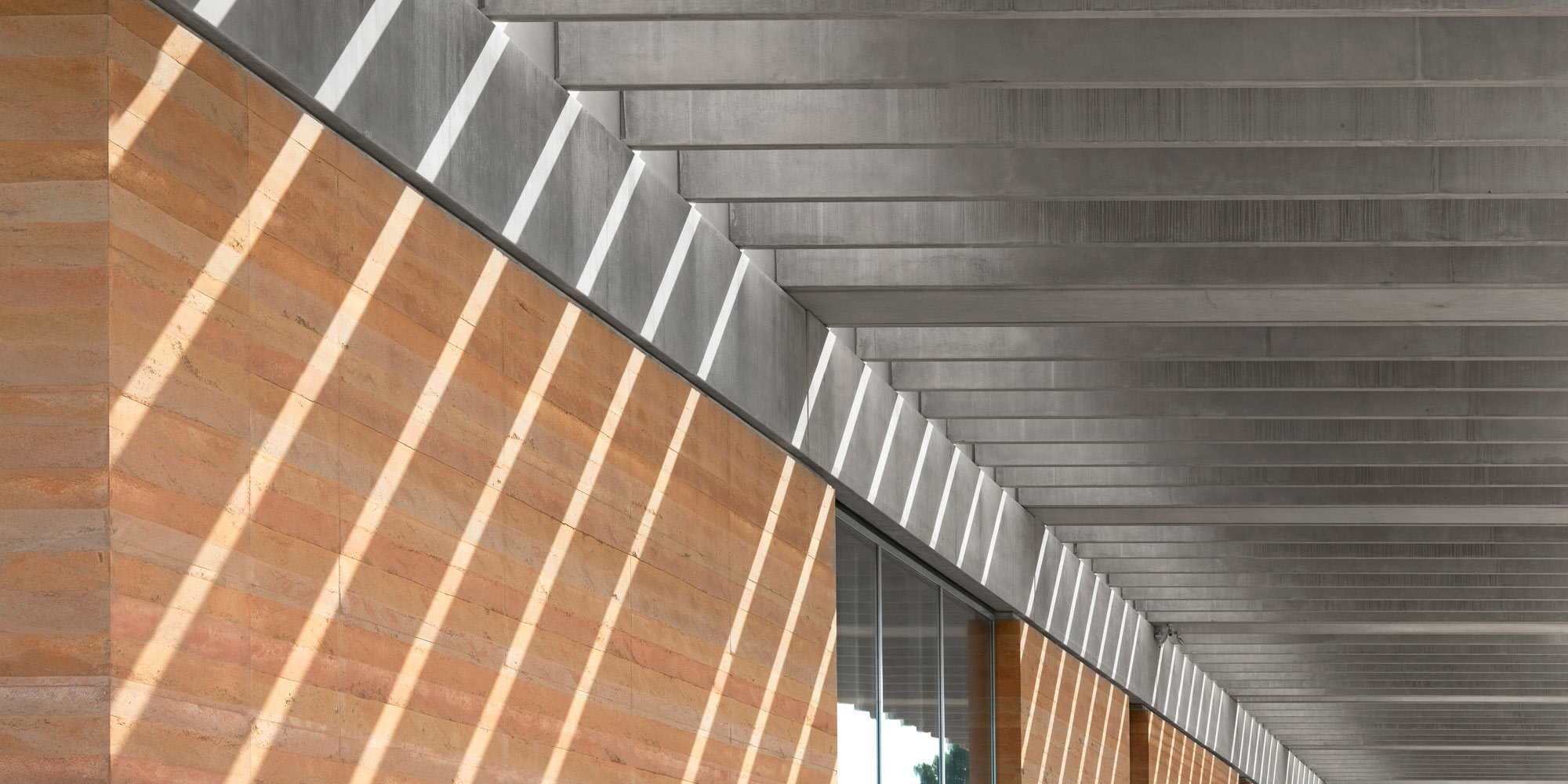
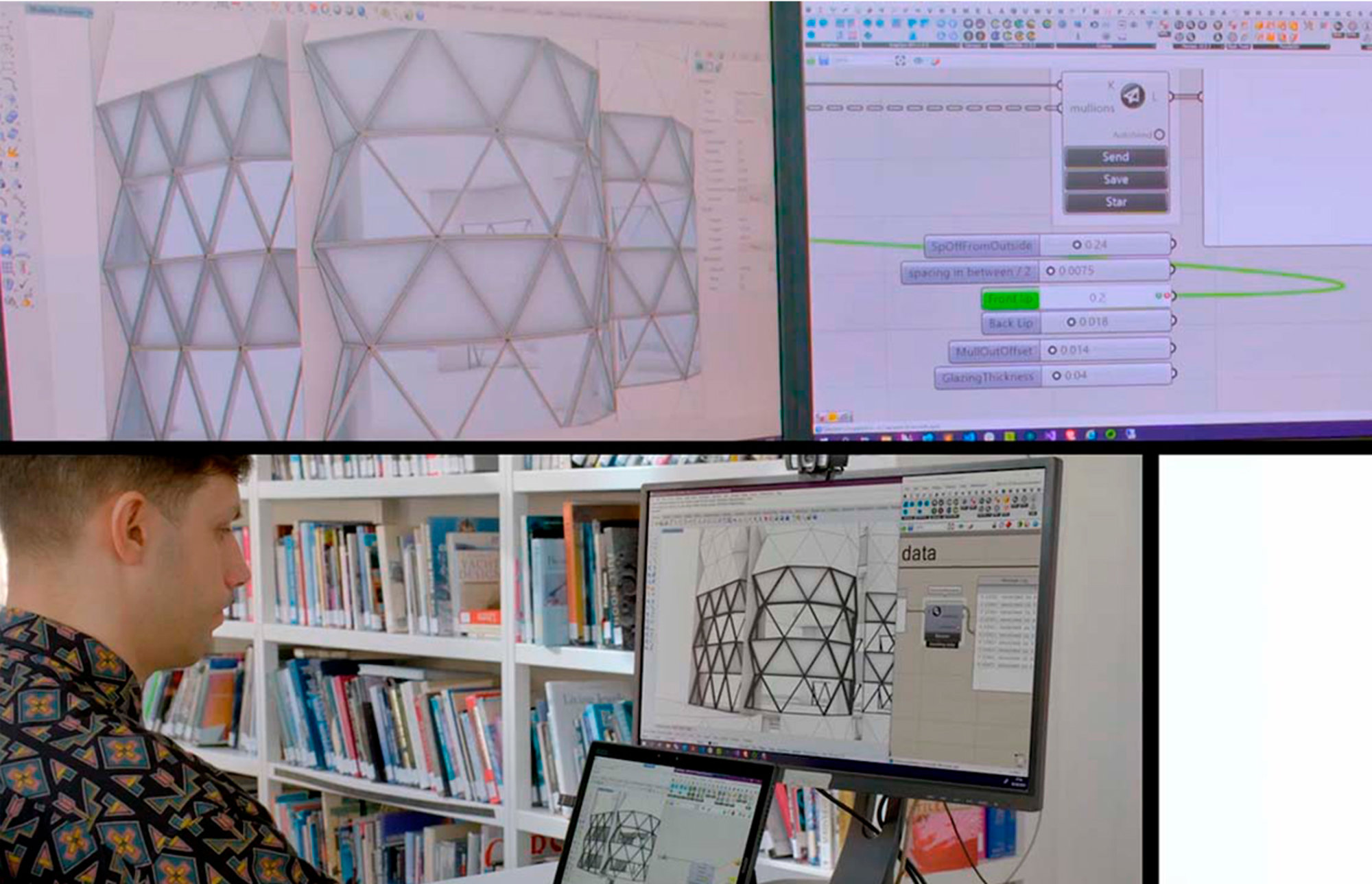
Complex Geometry and Fabrication
The team uses modelling, computation and manufacturing to help deliver innovative projects. They work with a remarkable variety of materials (wood, metal, glass and concrete) using fabrication techniques including computer-controlled cutting, bending, milling, and additive manufacturing. The expertise and the computational tools that have been developed in-house continue to inform new projects, undertaking research collaborations with universities to further enhance our knowledge about design and construction.
Alif – The Mobility Pavilion, Expo 2020 Dubai
Foster + Partners designed the first of the three signature pavilions for the Dubai Expo based on the sub-themes of Mobility, Sustainability and Opportunity. The façade features a series of horizontal stainless-steel fins that wrap around the building. These fins lift to form a canopy for each of the three entrances. The Applied R+D team was involved in the computational design of the louvers, ensuring that the geometry has a continuous flow across the whole façade.
O’Hare Global Terminal
The entire shell for the new proposed O’Hare terminal in Chicago was envisioned as a column-free space, comprised of a spaceframe with four landing points on each side, creating the impression of the entire roof almost floating over the concours. The entire shell was dynamically relaxed and its panelisation and frame optimised both in terms of structural stability and environmental requirements.
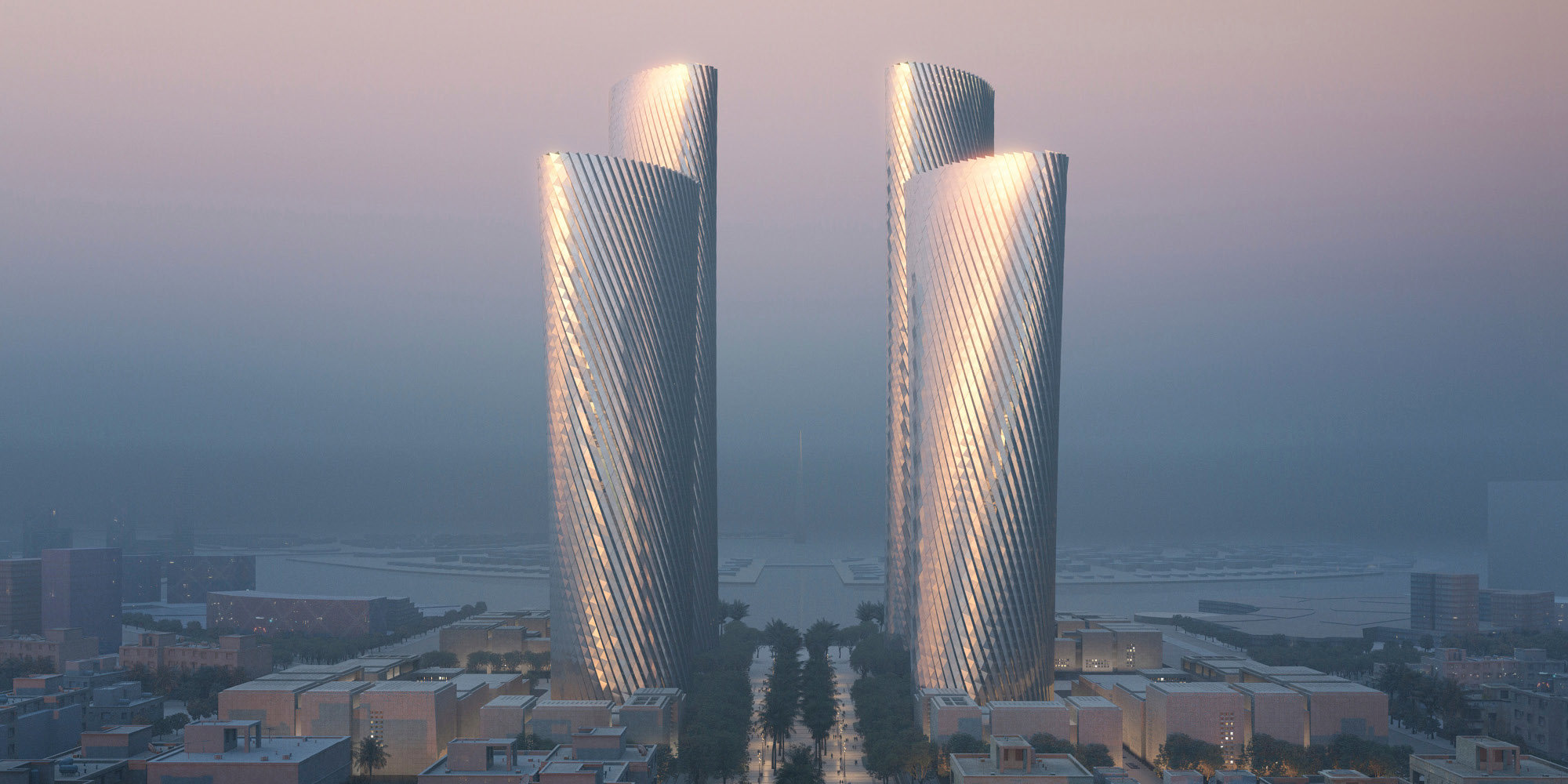
Lusail Towers
In 2017 Foster + Partners redesigned their 2007 proposed scheme for the Lusail Towers in Qatar. The cladding system has an inherent sustainability sensitivity as it is spiralling around the buildings in one direction responding to the sun path, achieving a ground-breaking wall-to-glass ratio for the location. The geometry of Lusail Towers is a result of series of interoperable parametric models using our internally developed software Hermes, where design data were exchanged in real time between disciplines and consultants in a vertically integrated fashion.
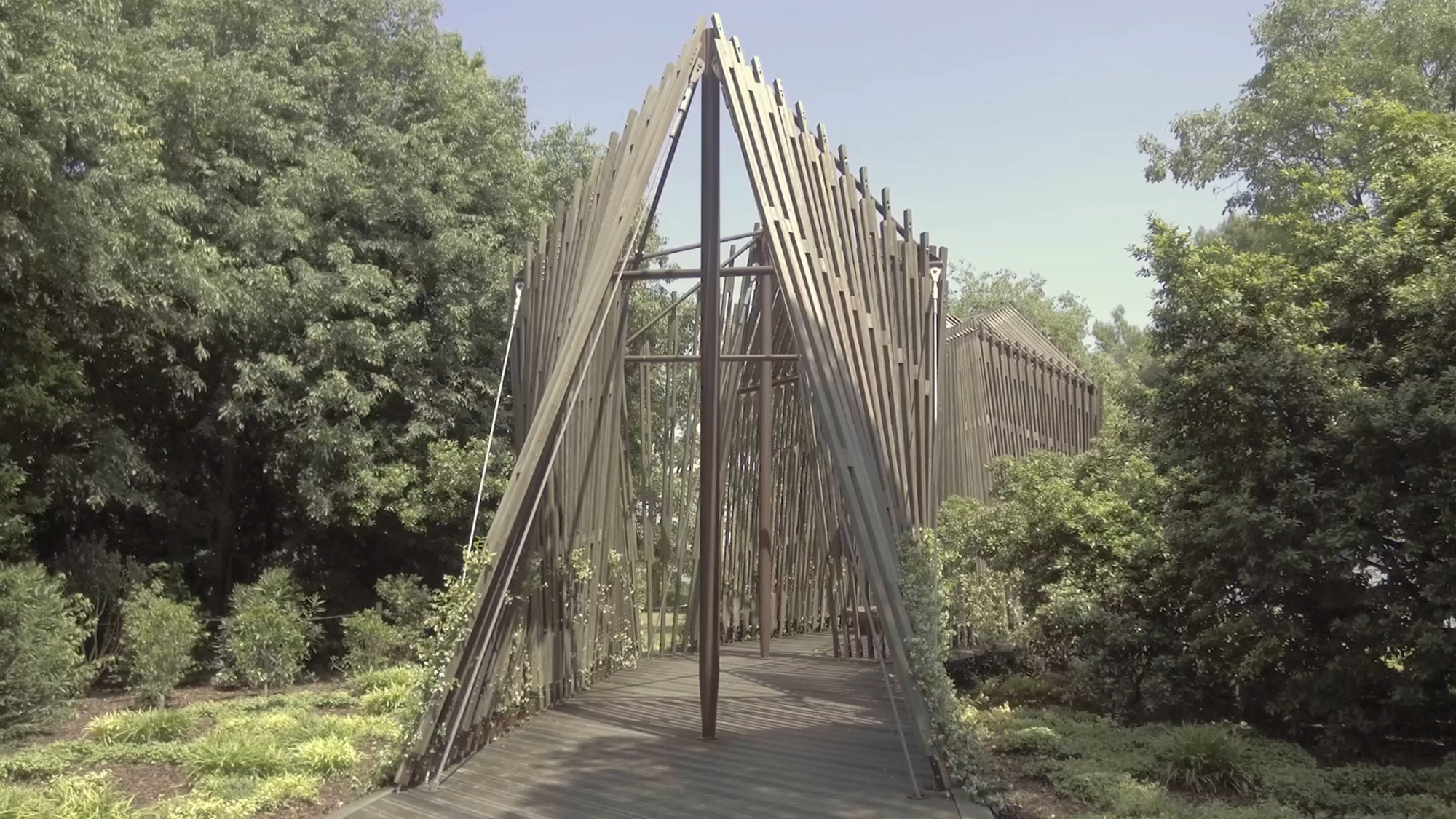
Vatican Chapel, Pavilion of the Holy See
The starting point for the chapel’s design concept was to take three symbolic crosses set in the landscape, draped with a tent-like membrane. As the design evolved, the crosses became a tensegrity structure of cables and masts, whilst the membrane developed into a wooden latticework attached to the structure. The Applied R+D group provided comprehensive parametric modelling and design-to-production support for the project. Changes to the structural model were reflected automatically in the cladding model and fabrication documentation.
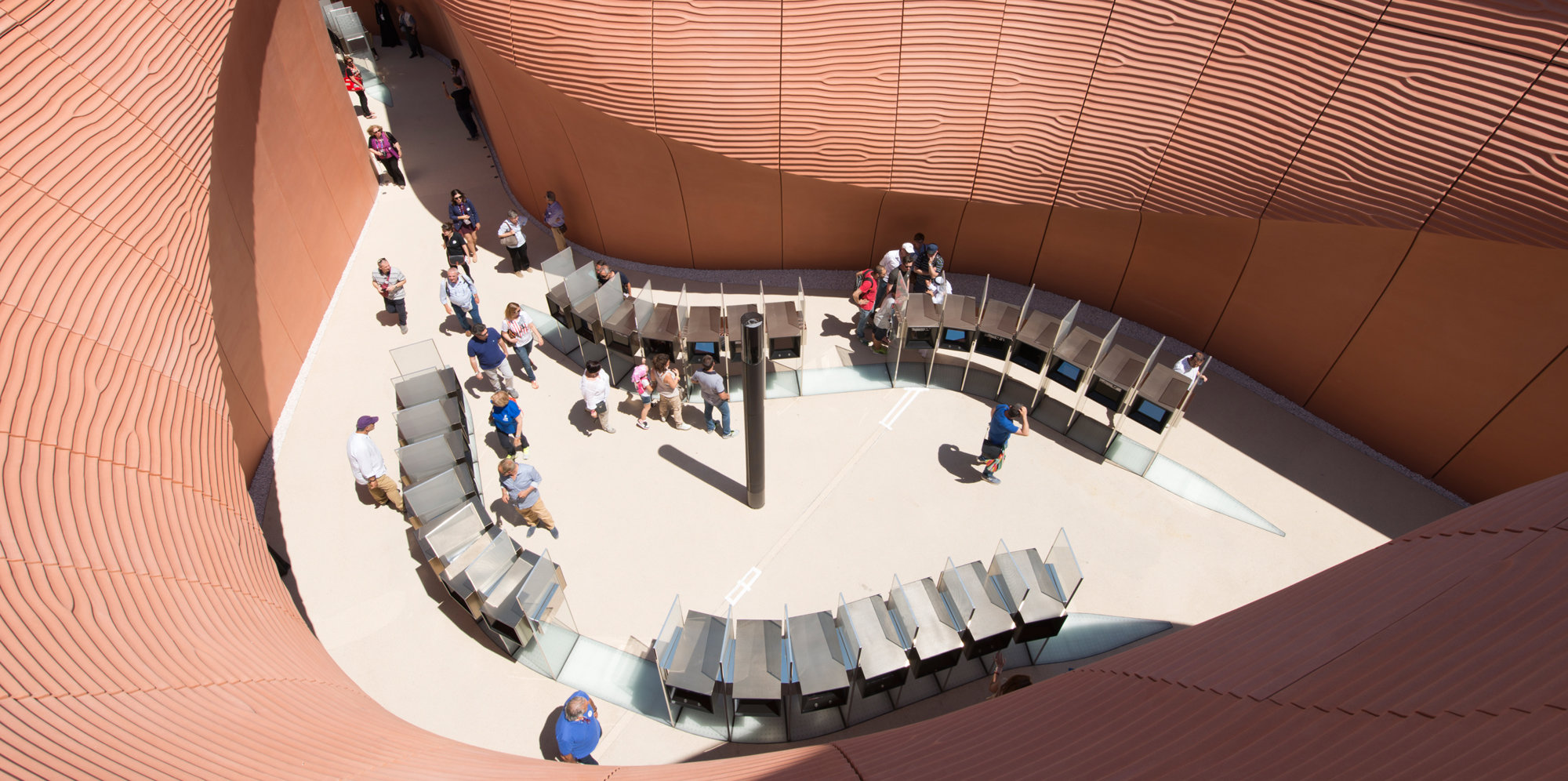
UAE Pavilion Milan Expo 2015
From its inception the design of the pavilion was intended to evoke the undulating surfaces of sand dunes in the Emirates. The Applied R+D team worked closely with the design team to deliver GRC wall panels that used a pseudo-random ripple pattern to balance randomness with the need for repetition. The precision of the digital models allowed the contractor to use them directly for computer-controlled fabrication.
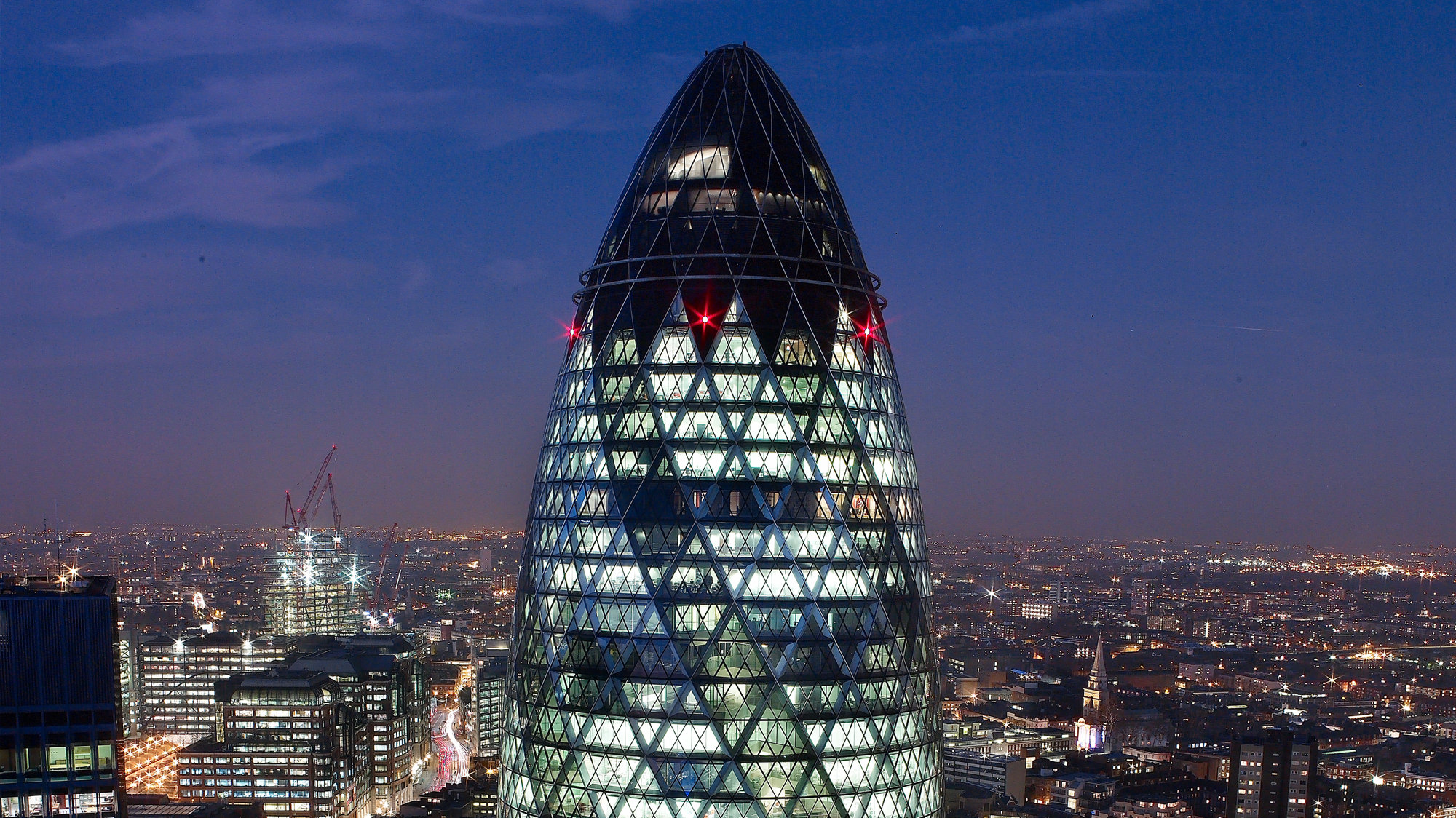
30 St Mary Axe
London’s first ecological tall building designed for Swiss Re is rooted in a radical approach − which was deliver through bespoke parametric design software that was well ahead of its time. All critical aspects of the building's form were numerically controlled by members of the design team and changes to key parameters would automatically regenerate the design model and documentation.
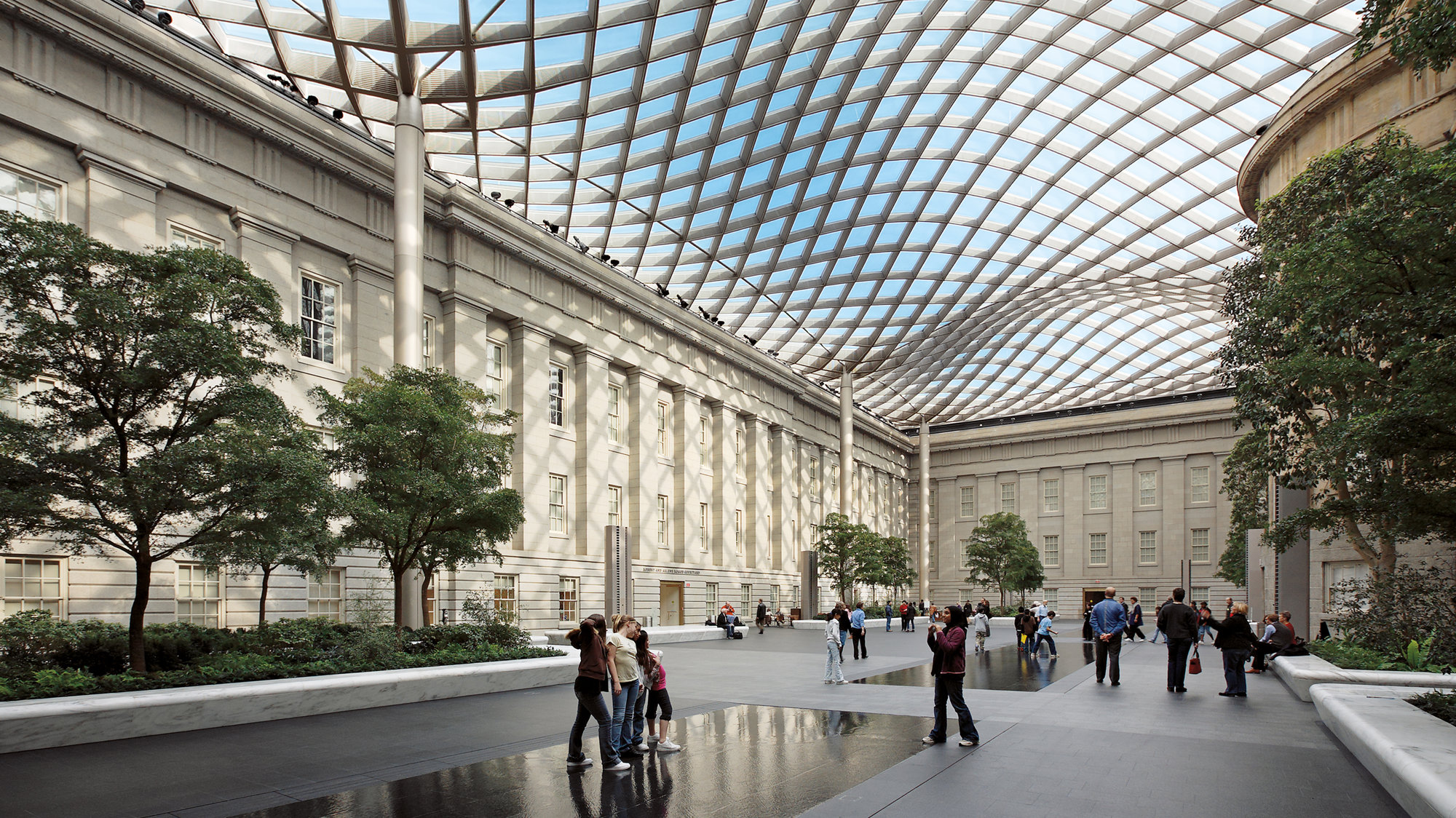
Smithsonian Institution Courtyard
For each iteration of the Smithsonian design, powerful bespoke software generated dedicated models for structural and acoustic analysis, visualisation, and eventually fabrication information. Optioneering allowed for designers to make informed choices about the combination of physical characteristics of the design.
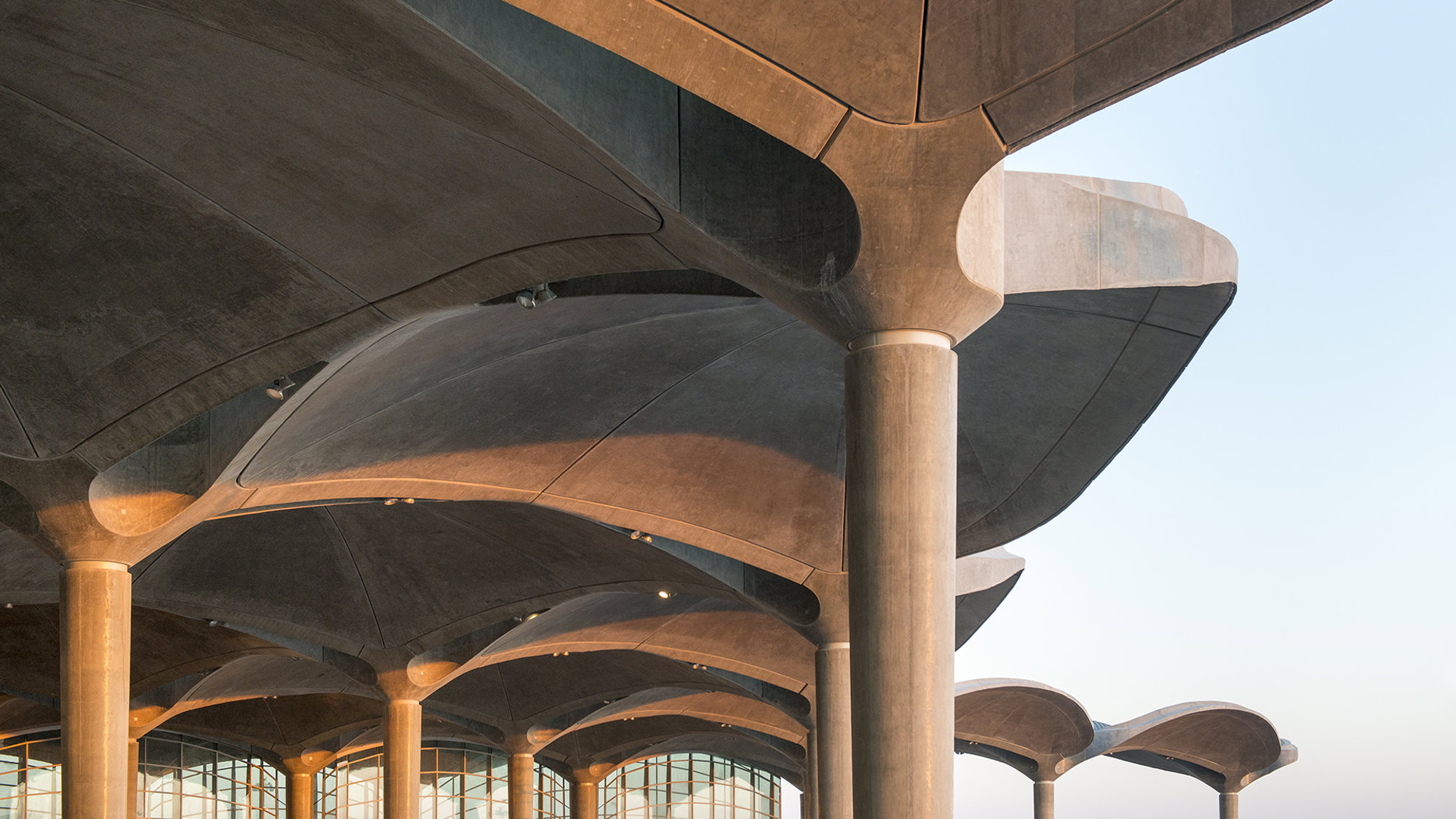
Queen Alia International Airport
The new terminal for Queen Alia International Airport broke new ground for the practice in modular design and the use of concrete as the predominant material. The Applied R+D team helped to solve the complex geometric challenges in ensuring smooth curvature across the enormous roof shells. Custom drawing extraction software allowed for providing thousands of sections for the formwork direct to the fabricators.
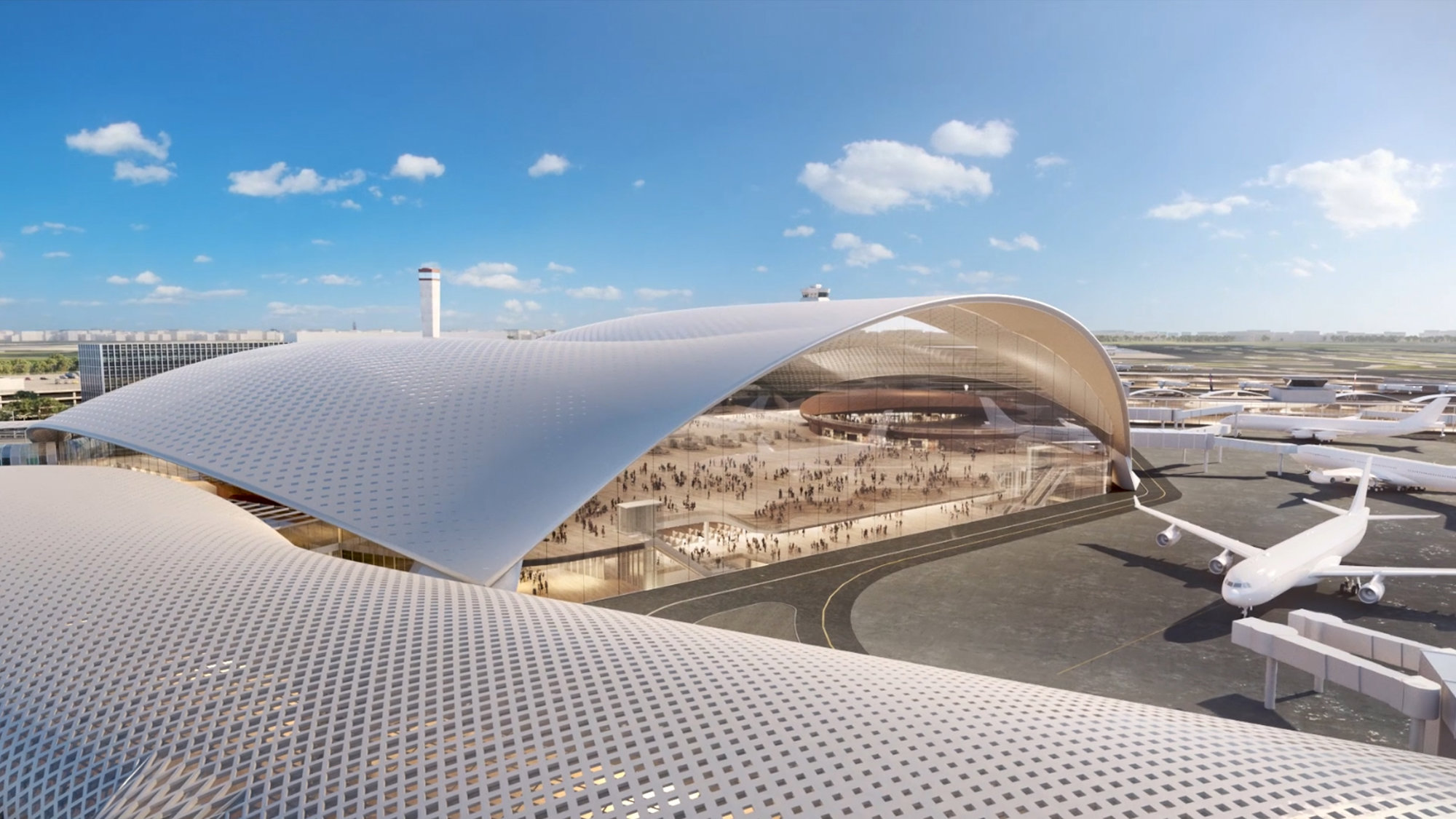
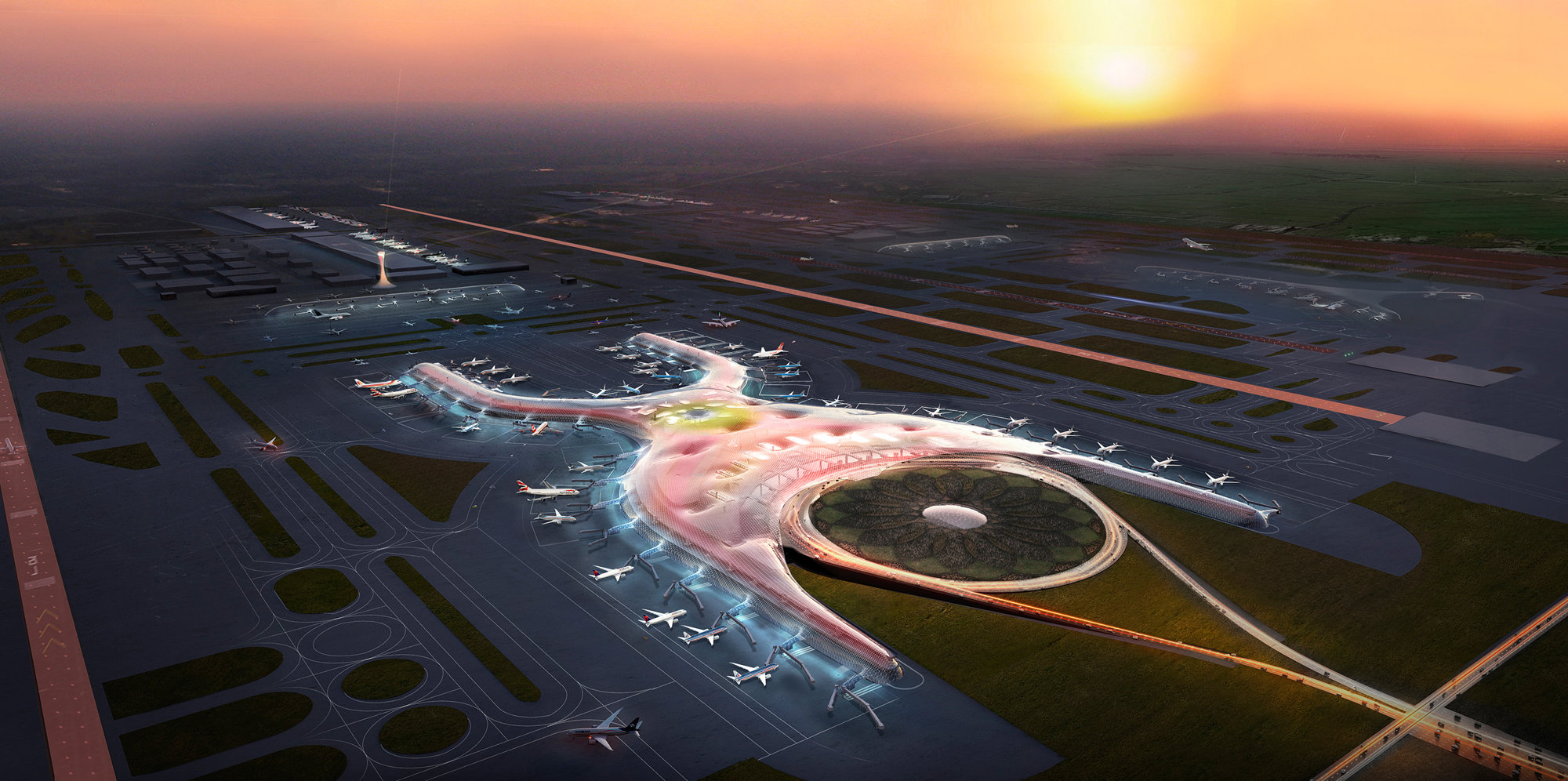
New International Airport Mexico City
At 743,000 square metres, Mexico City International Airport was slated to be one of the world’s largest airports revolutionising airport design. The entire terminal is enclosed within a continuous lightweight gridshell, embracing walls and roof in a single, flowing form, evocative of flight. The Applied R+D team was involved with the development of the roof for the competition-winning entry. The roof was form found using computational methods and then dynamically relaxed.
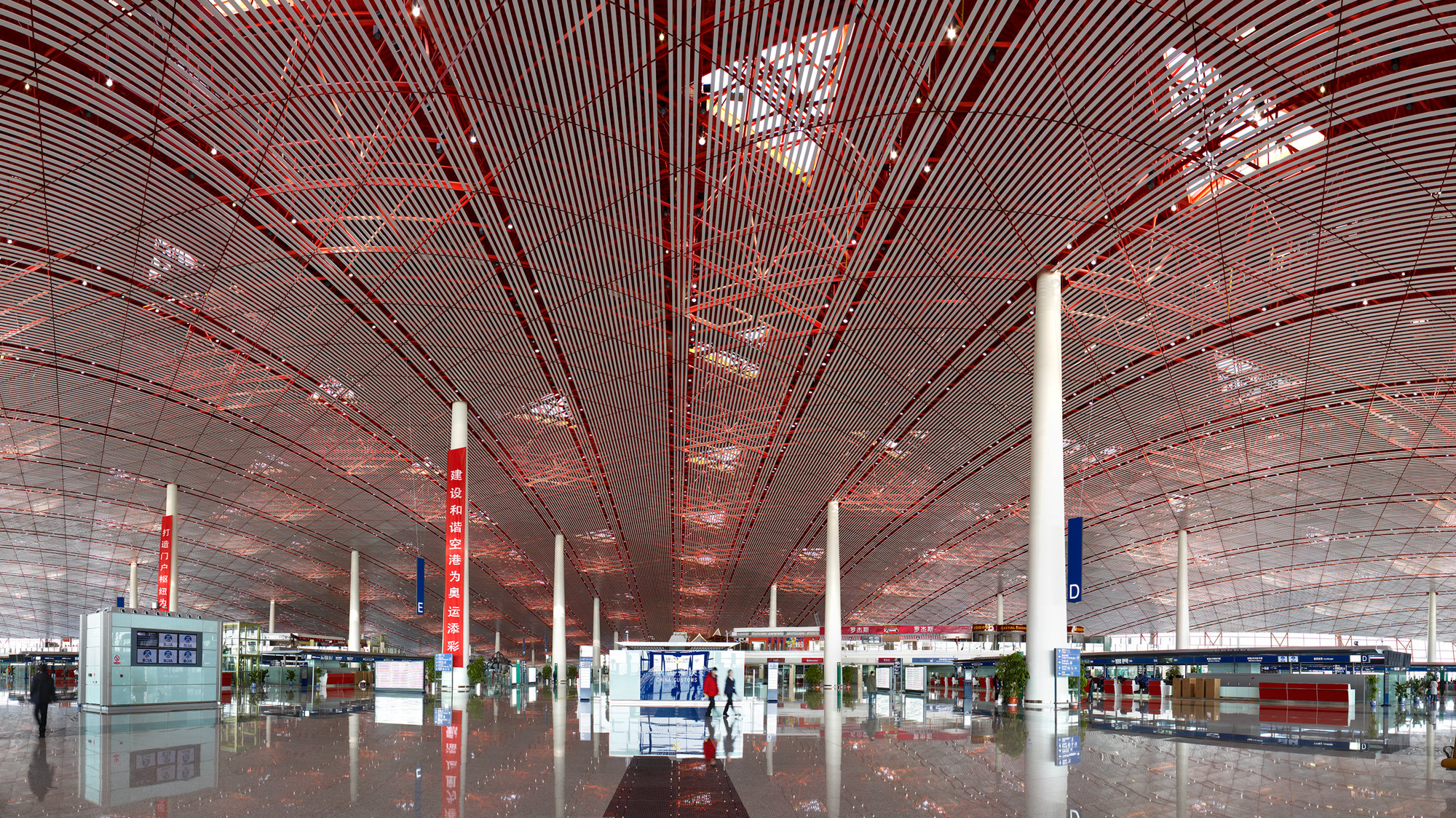
Beijing Capital International Airport
Completed as the gateway to the city for the twenty-ninth Olympiad in 2008, Beijing's international terminal is the world's largest and most advanced airport building − not only technologically, but also in terms of passenger experience, operational efficiency and sustainability. Three kilometres long, BCIA remains one of the largest computational generated roofs in the world. Custom software was written by the Applied R+D teamgroup to generate the geometry of the spaceframe roof and facades in an extremely compressed timeframe.
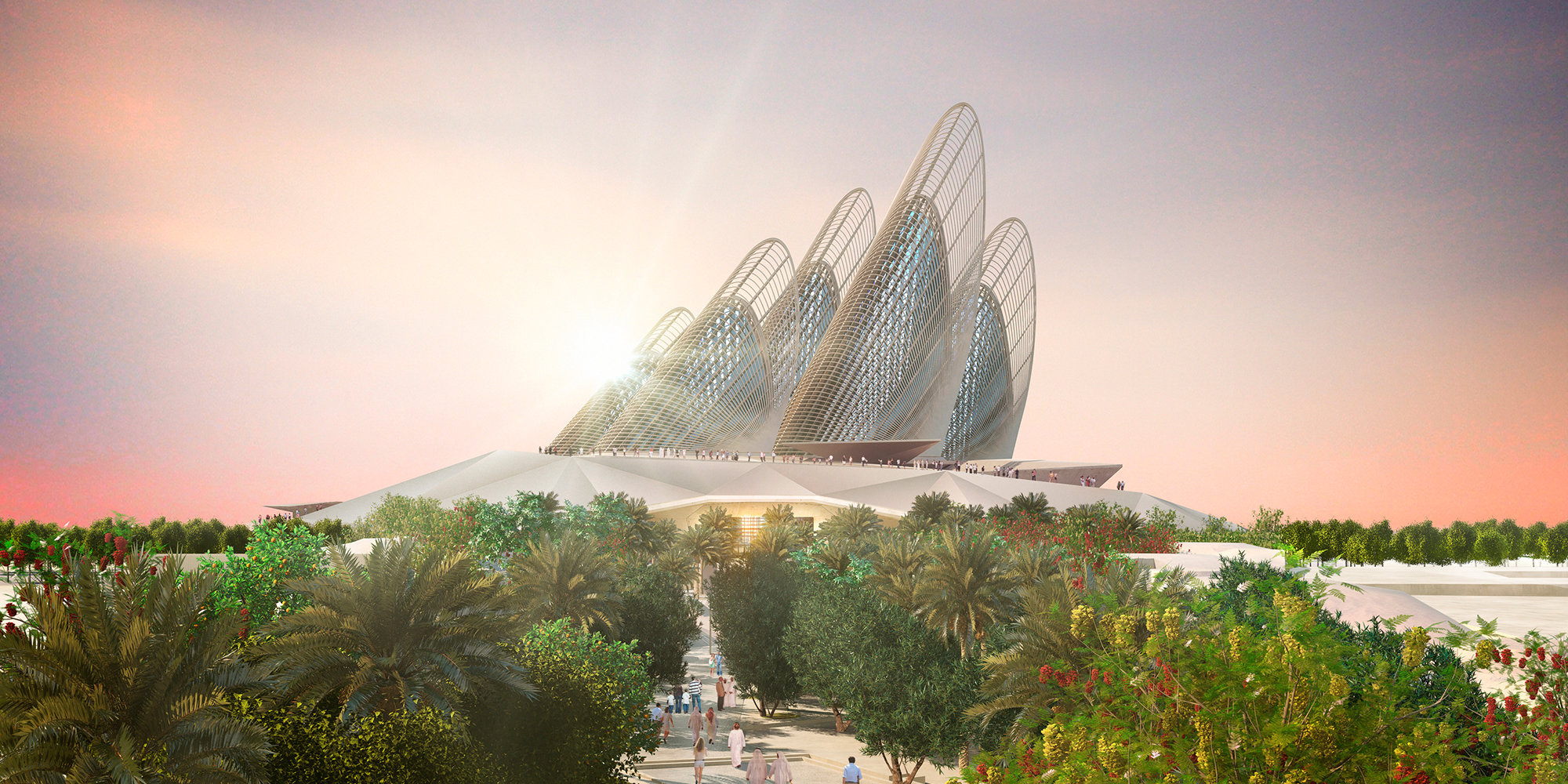
Zayed National Museum
Conceived as a monument and memorial to the late Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan, the Zayed National Museum will be the centrepiece of the Saadiyat Island Cultural District. The design for Zayed National Museum required incorporating 3D modelling and computational design from the design team, Applied R+D team and the consulting engineers. Numerous 3D and data models allowed for updating the design and documentation of the sophisticated wing and pod components that will be central to the museum experience.
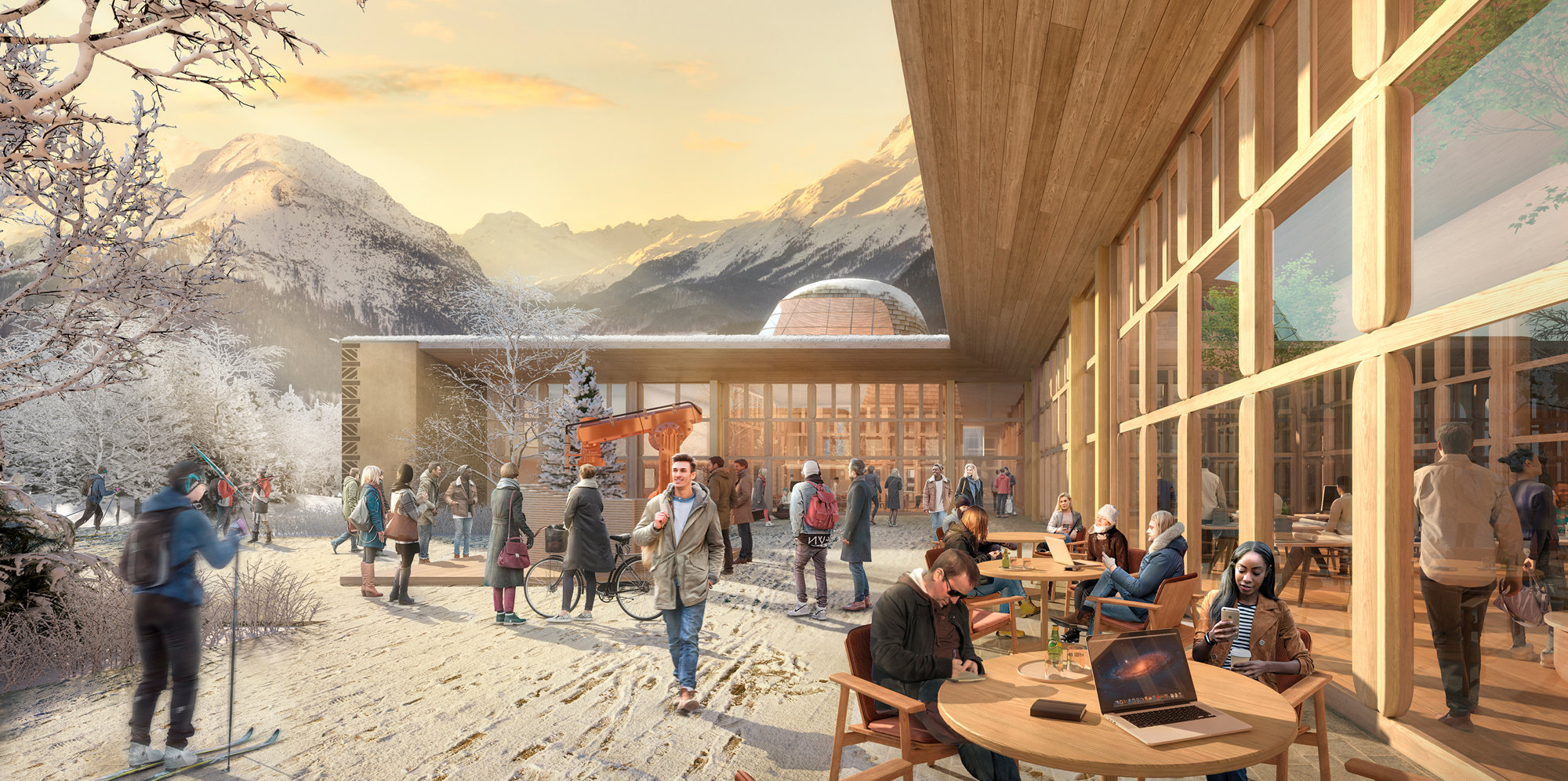
Innhub La Punt
InnHub La Punt is a new centre for innovation in the heart of the Engadin valley. The roof has been carefully designed to combine renewable energy generation systems, arranged on angled surfaces to avoid snow accumulation, while allowing daylight to enter the deepest parts of the building. A parametric model of the roof was thus developed, in order to post-rationalise and standardise the dome’s geometry for fabrication purposes.
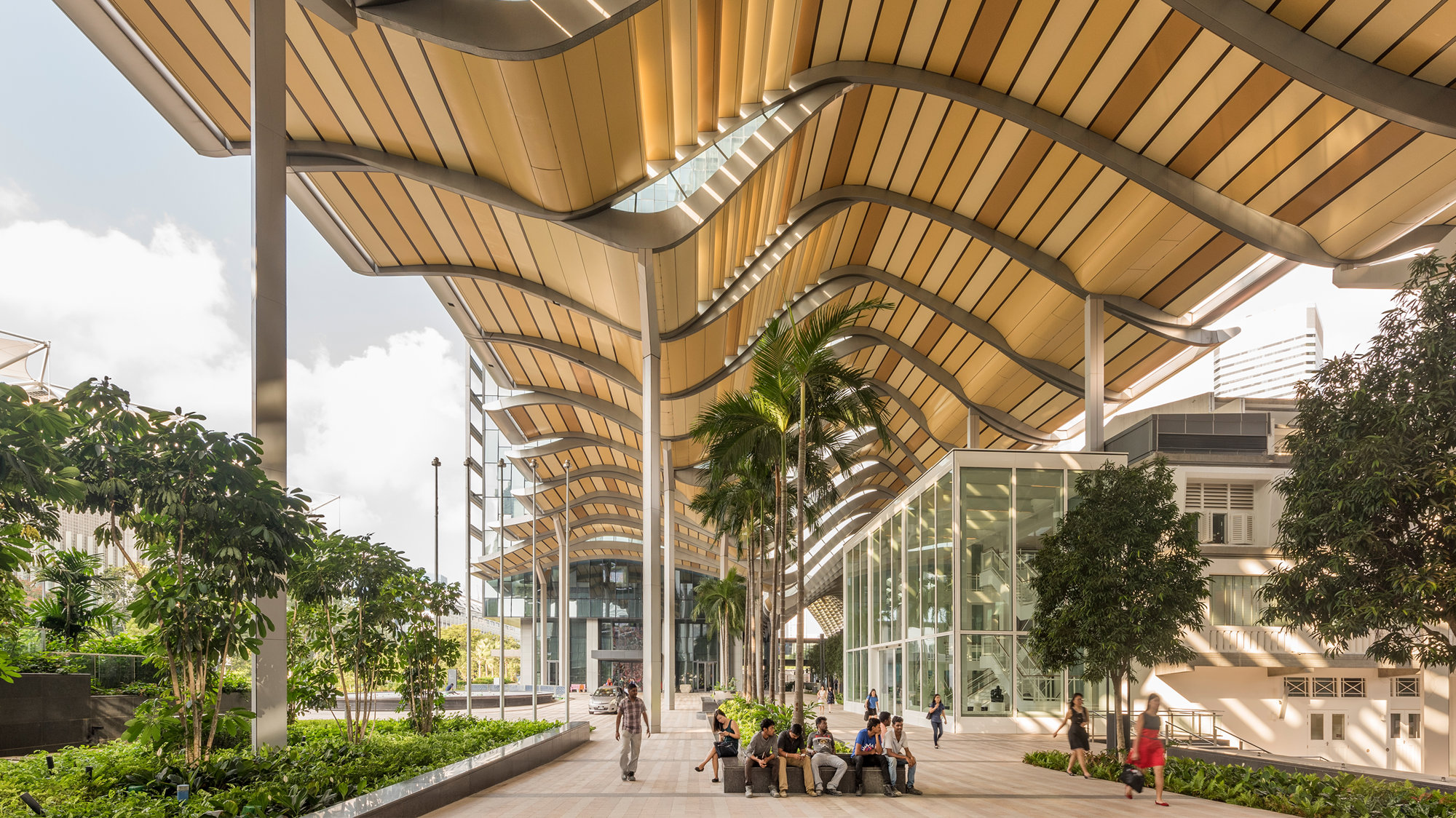
South Beach
The South Beach development covers an entire city block between the Marina and Civic District in the heart of downtown Singapore. The canopy consists of a range of component modules with different angles and overlaps to promote shading, ventilation and rain protection. Custom software written by the Applied R+D team linked design team changes of the undulating canopy surface to the desired mix of canopy components enabling hundreds of iterations and refinements to the design.
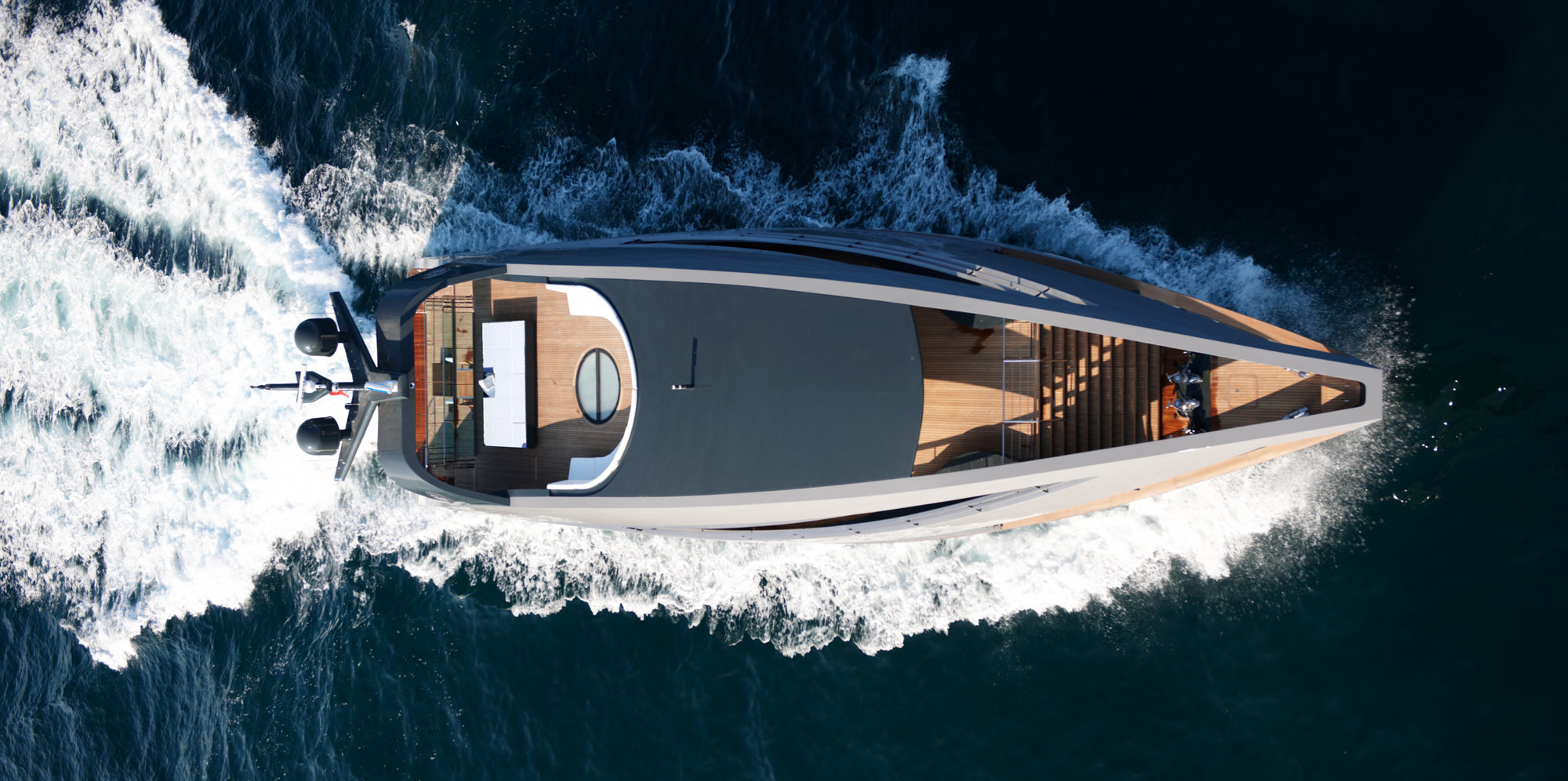
The YachtPlus Fleet
The 40-metre, long-range cruising yachts for the YachtPlus offered a great testbed for members of the Applied R+D team to use cutting-edge technology of the time to develop the design along the team. Parametric tools allowed for the precision-control of the shape, ensuring G1 continuity with the hull, while CFD was employed to analyse the shape.
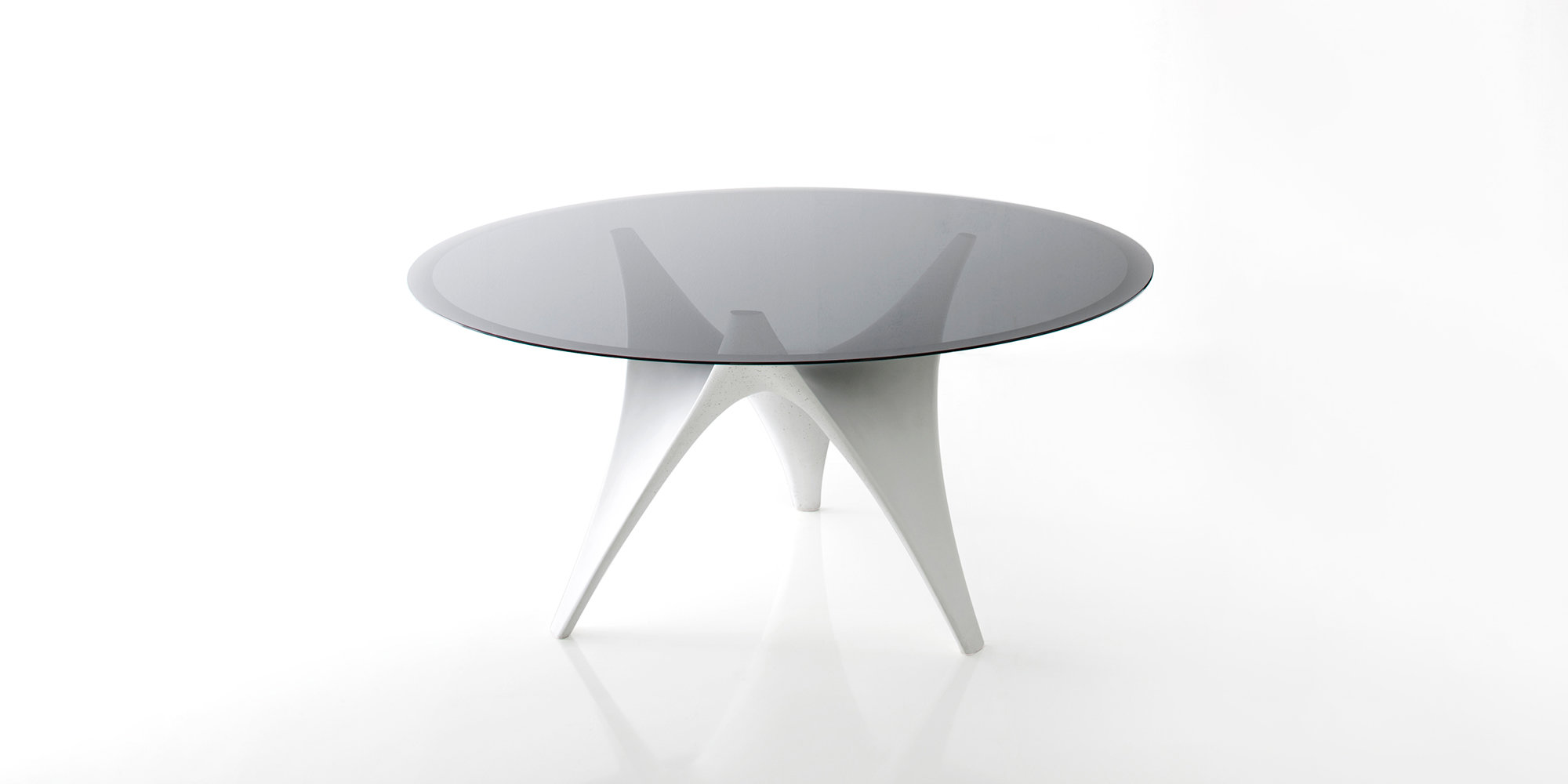
Arc, Molteni&C
The base of the Molteni Arc is a hyperbolic surface, acting solely in compression, allowing it to be manufactured out of thin shell concrete. Creating the formwork for this concrete required exceptional control of digital modelling processes. The Applied R+D team contributed expertise in structural form-finding and parametric design to ensure a high level of quality throughout the design process.
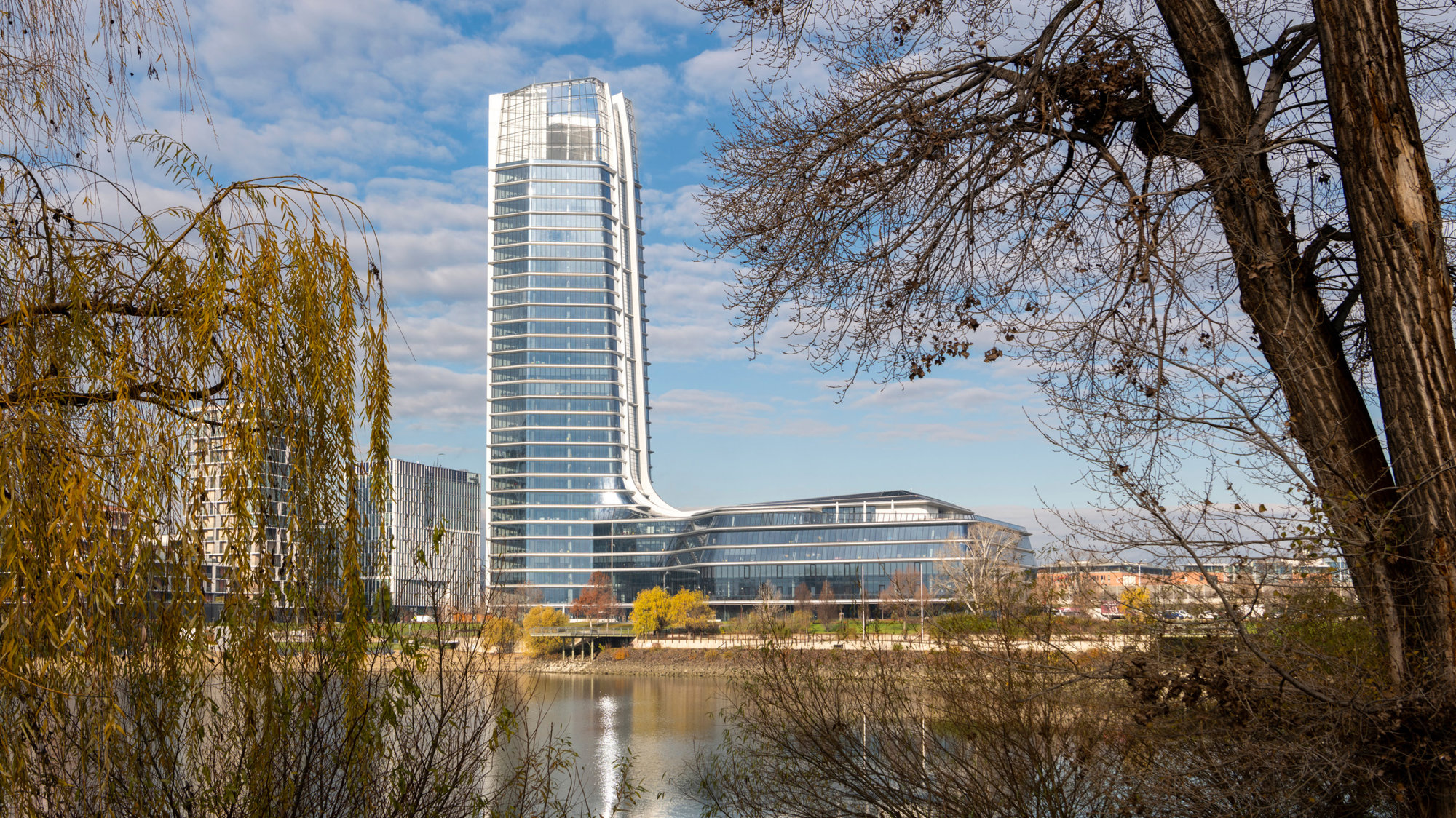
MOL Headquarters
The Applied R+D team contributed to the design and rationalisation of the MOL Tower's facade – slated to be the tallest building in Budapest. Close collaboration with both design and BIM teams since inception resulted in a design which is not only iconic but also highly optimised for digital fabrication. The complex and challenging form of the building is predominantly constructed from flat and easily manufactured panels while keeping the curved ones only where they are truly needed.
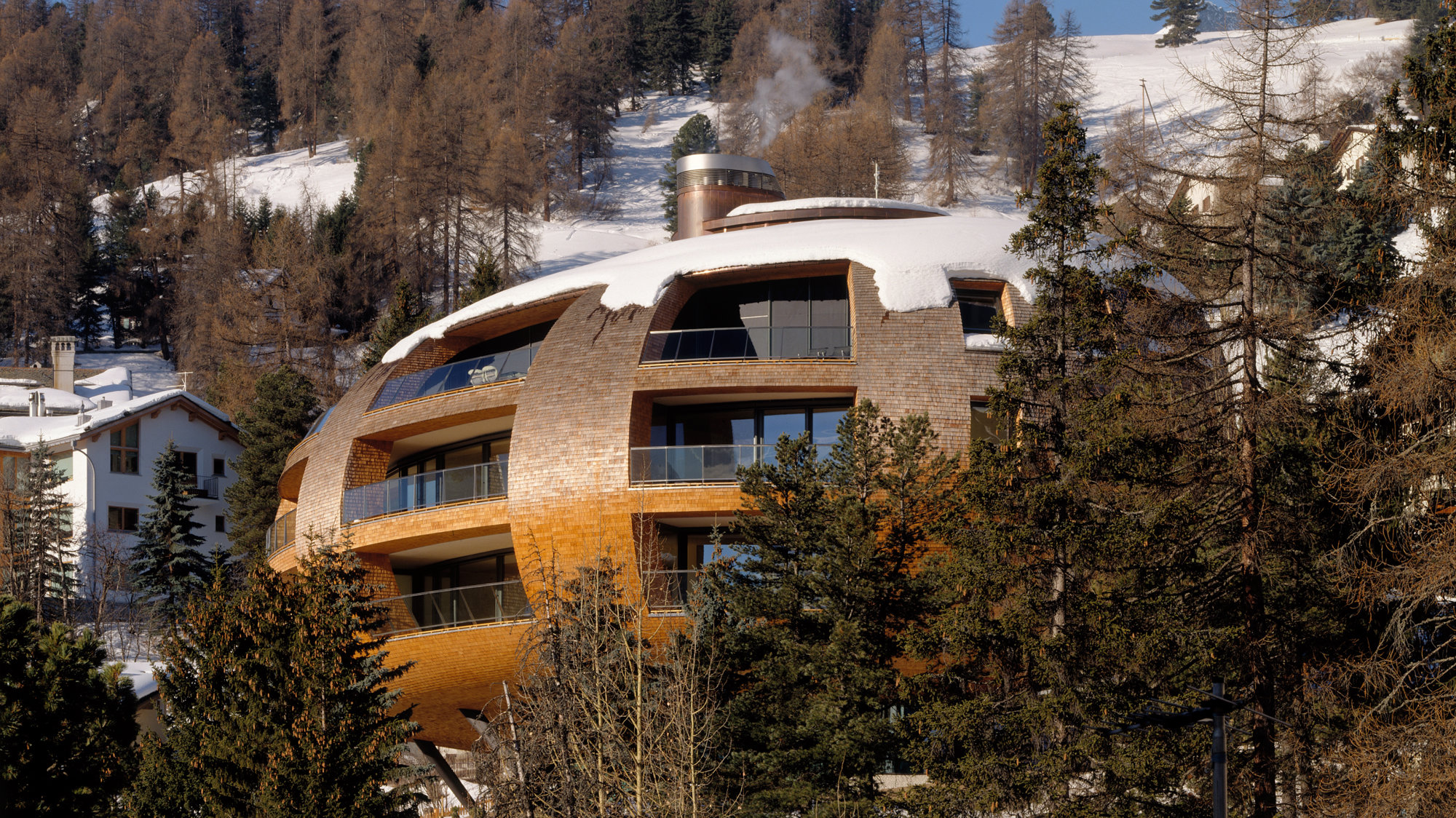
Chesa Futura
Chesa Futura ('house of the future' in Romansch) fuses state-of-the-art computer design tools with centuries-old construction techniques to create an environmentally sensitive apartment building. Custom software generated a detailed parametric model, closely integrated with the fabrication process to deliver a pioneering timber building on a very constrained site.
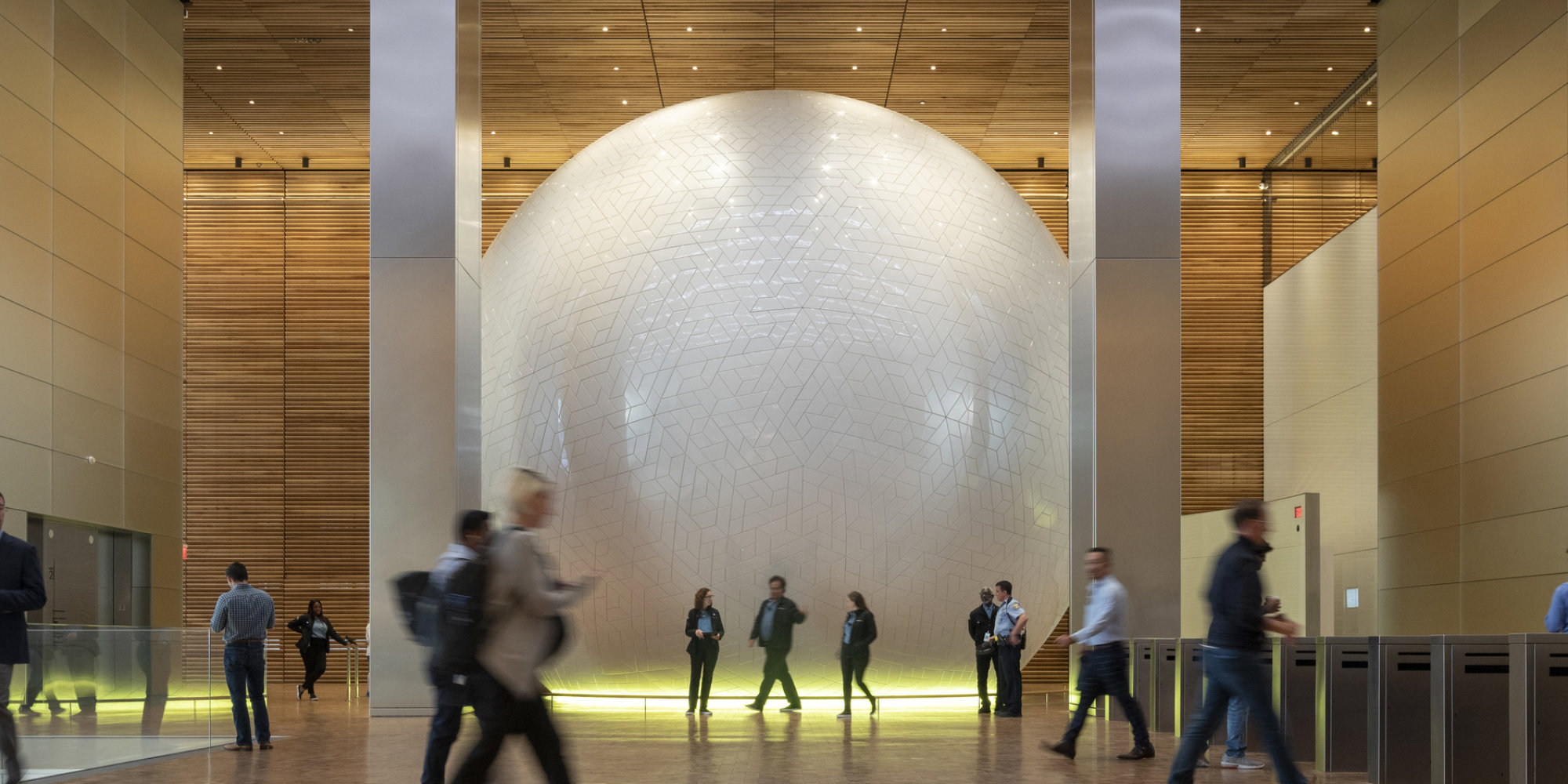
Comcast Universal Sphere
Located in the lobby of the Comcast Technology Center, is The Universal Sphere™, a structure that houses a unique cinematic experience created by Steven Spielberg for all ages, exploring the power of ideas. The Applied R+D team helped design and generate the geometry of exterior panels of the sphere. The panels are designed with repetition in mind, reducing the number of moulds needed for production while having a continuous seamless flow of the geometry.
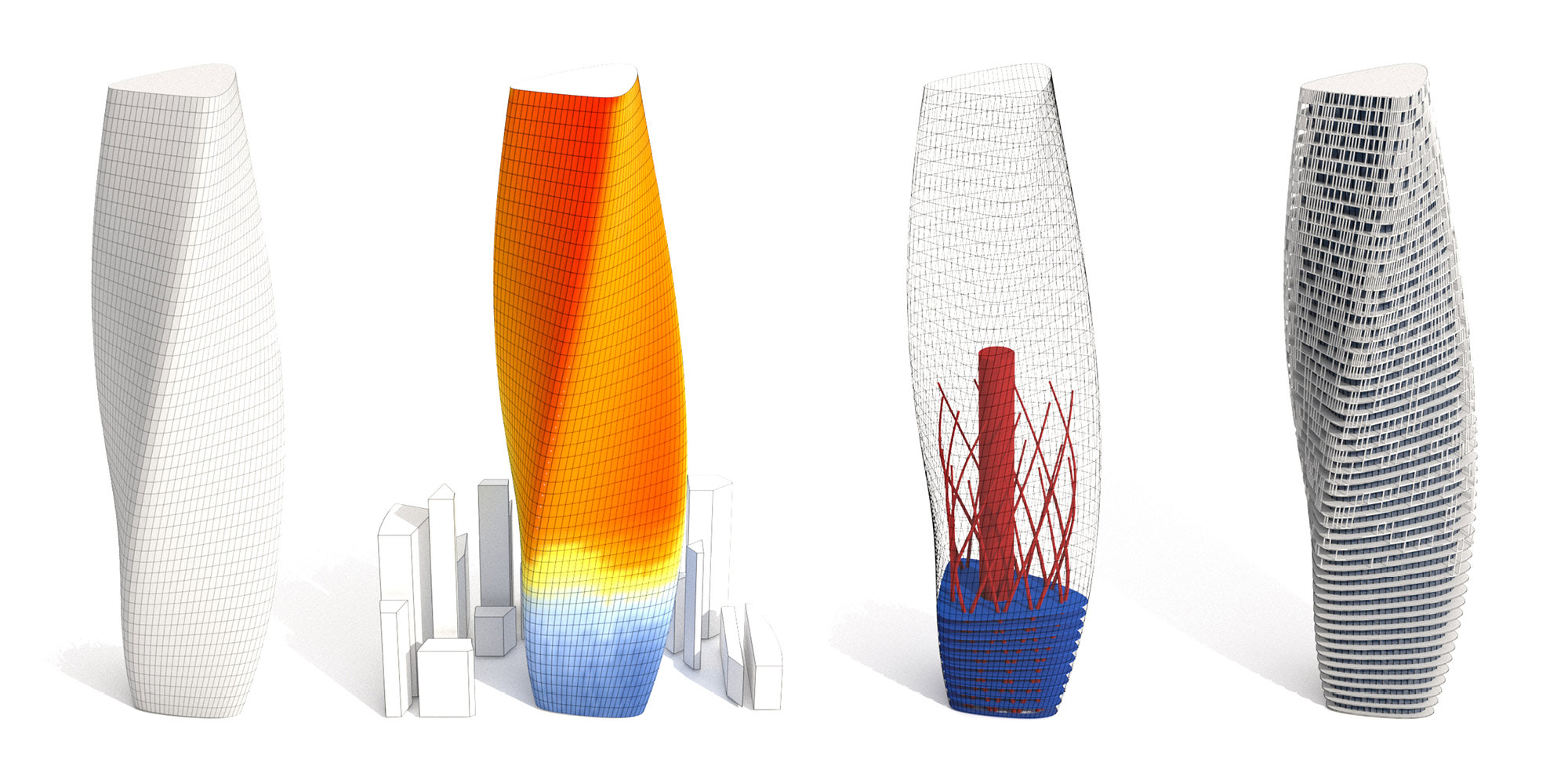
Performance Driven Design and Optimisation
The work of Foster + Partners has always embraced the needs and constraints of a building as opportunities - "drivers" - for innovative design solutions. With technology on our side, we are able to model these constraints more accurately to test our designs before construction begins. This allows us to study what happens as we change the factors that influence a design ("Performance-Driven Design") and it also allows us to find best solutions for particular design challenges ("Optimisation").
Cyclops
Cyclops is an environmental analysis plugin for Grasshopper in Rhino 3D developed by Foster + Partners. It significantly accelerates raytracing-based simulations by leveraging state-of-the-art GPU computing.
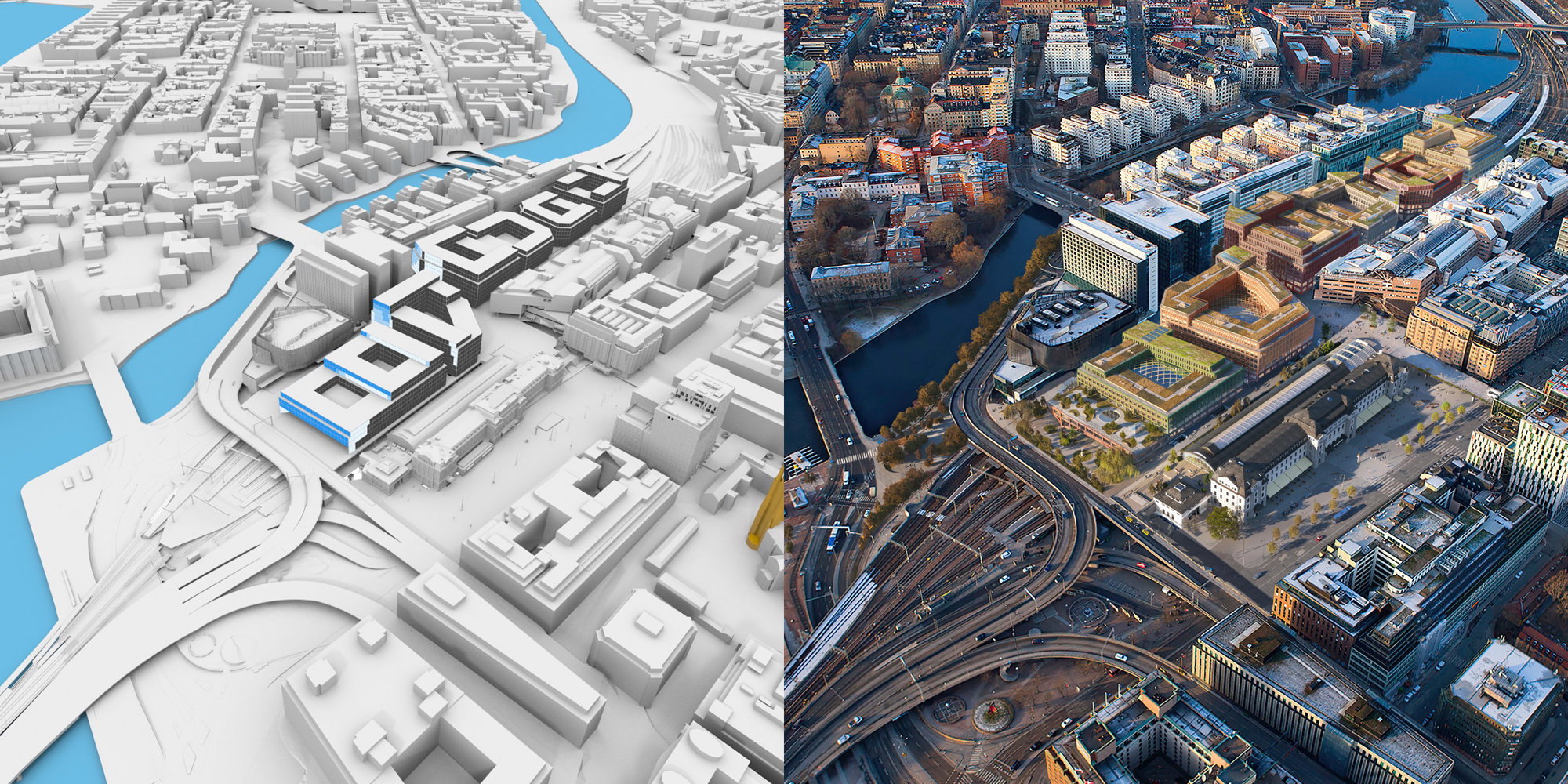
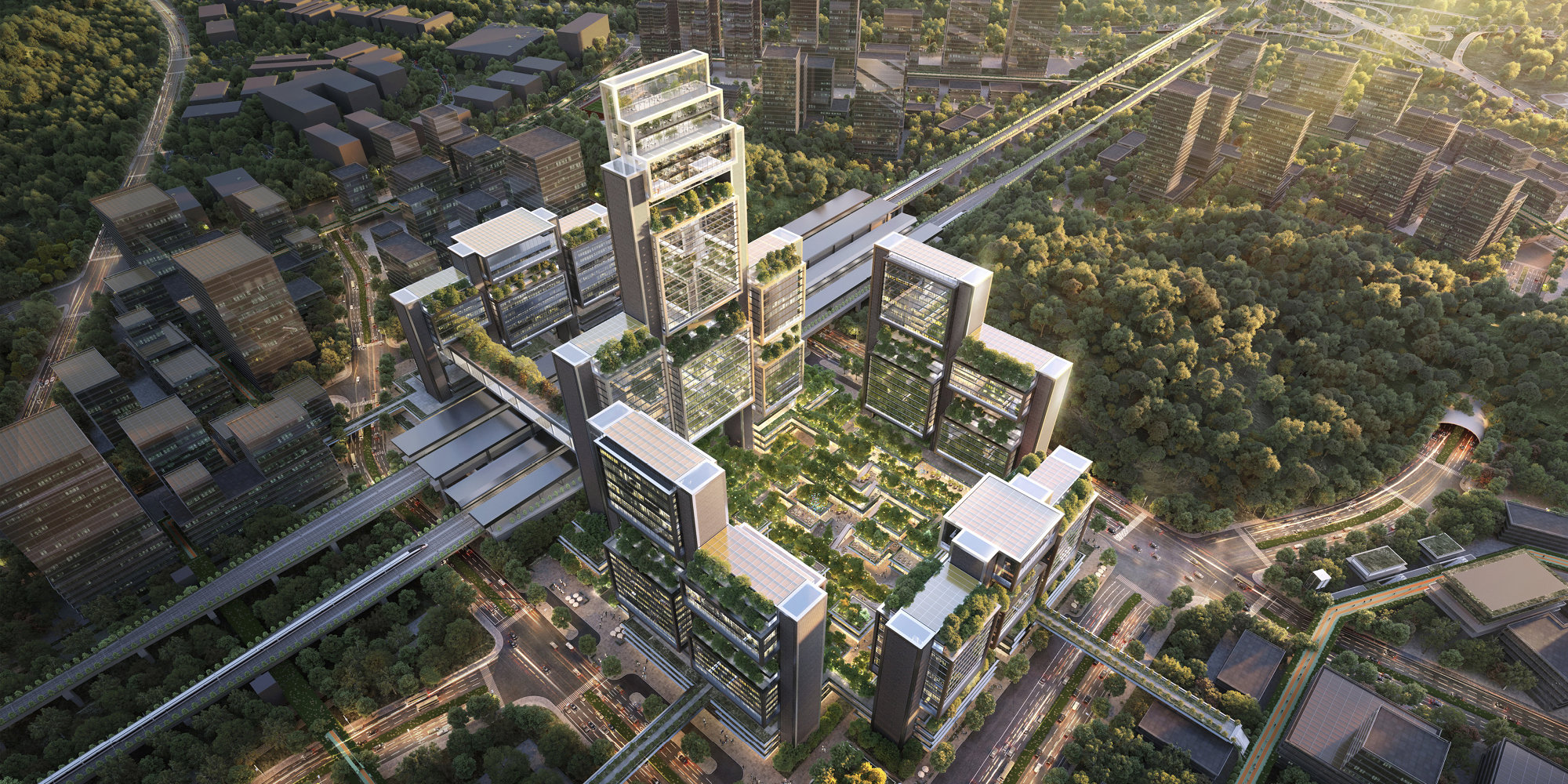
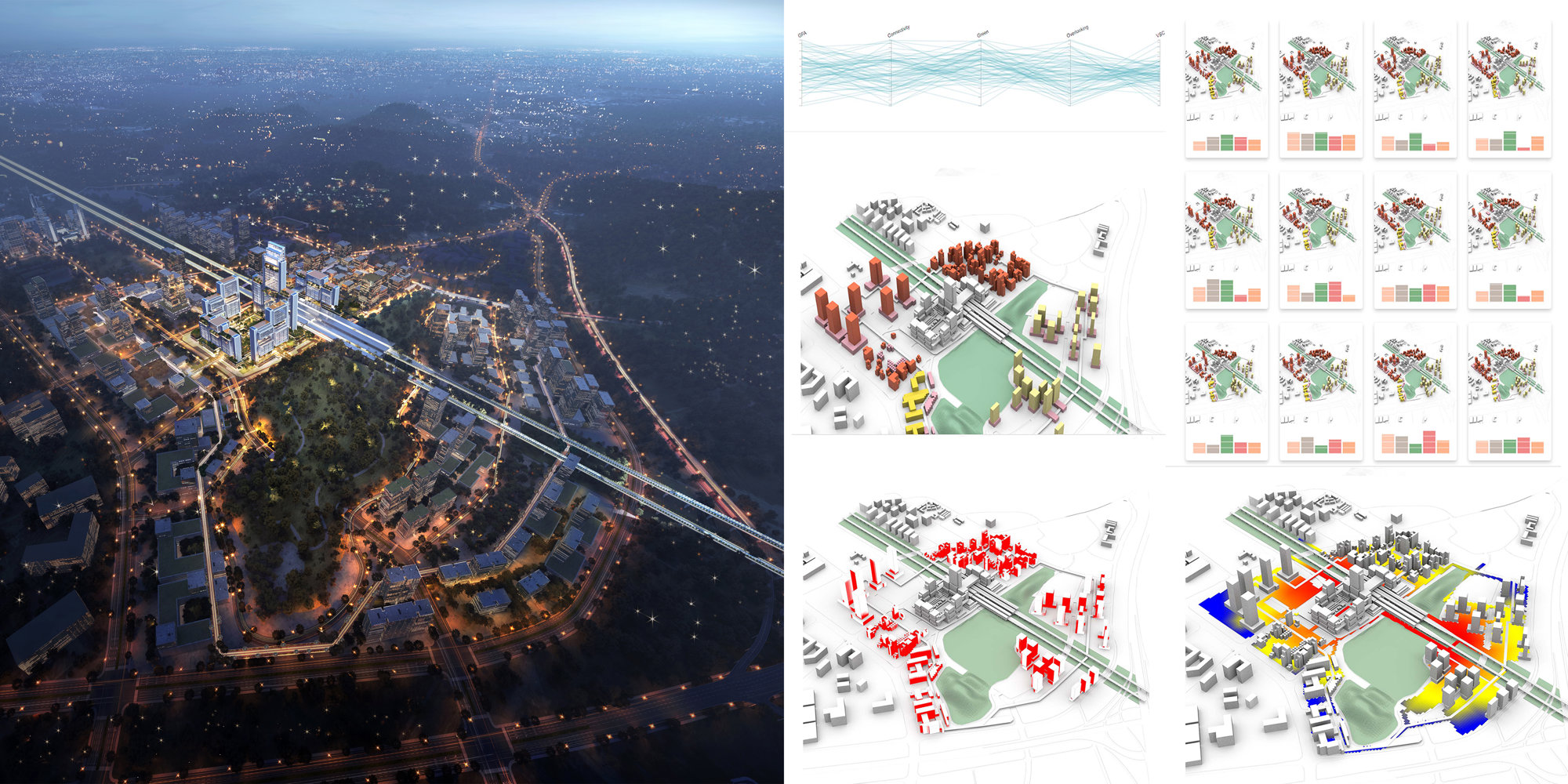
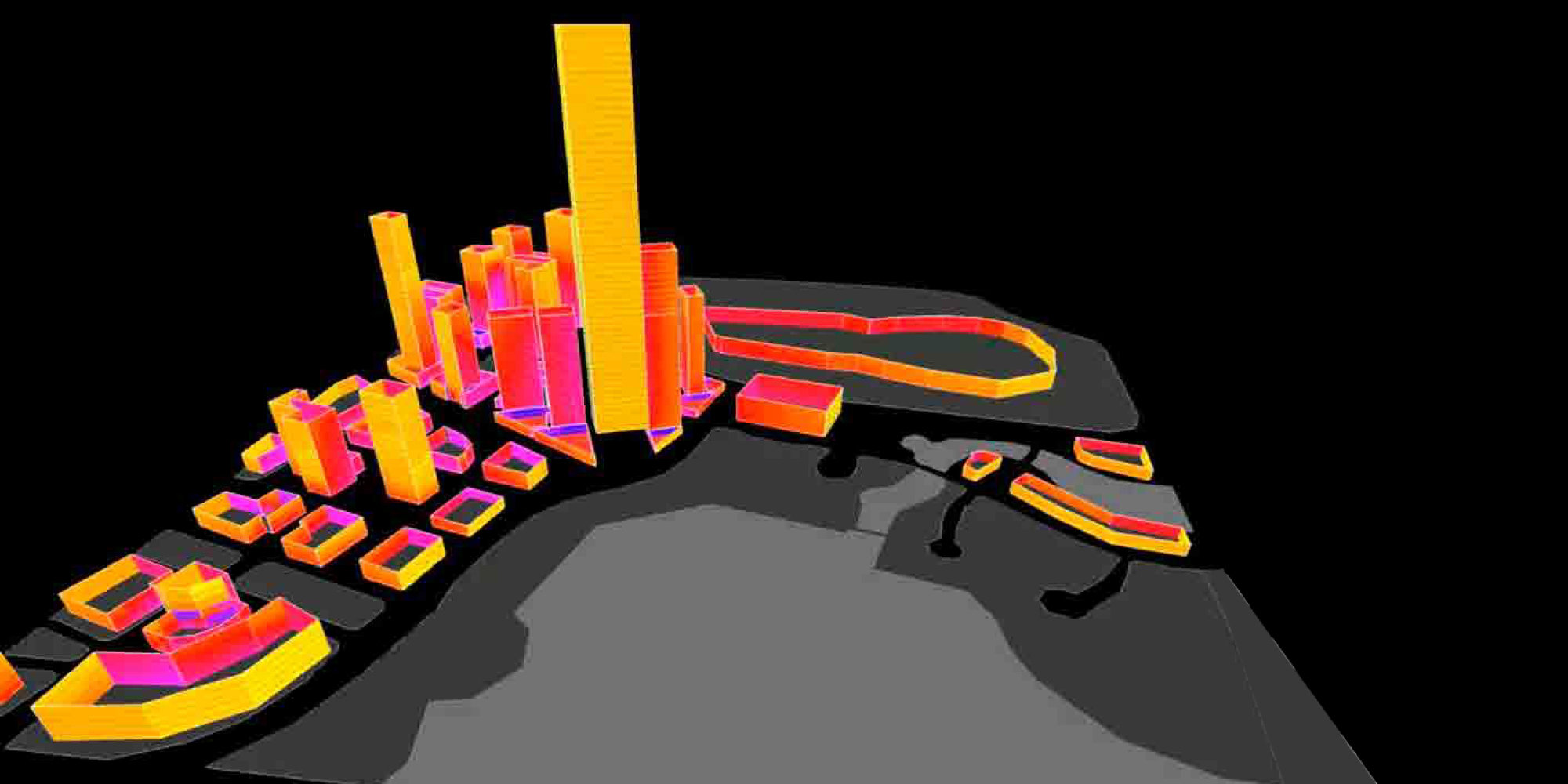
Guangming Hub, Hydra
Guangming Hub is a new Transport Oriented Development situated on the high-speed rail link that connects Hong Kong, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou. Based on the brief, the team identified a set of key objectives and constraints which would drive the initial placement of urban massing to positively influence urban growth in the region. a Hydra-generated massing was used as an inspiration and starting point for the team’s design explorations towards the production of the final model.
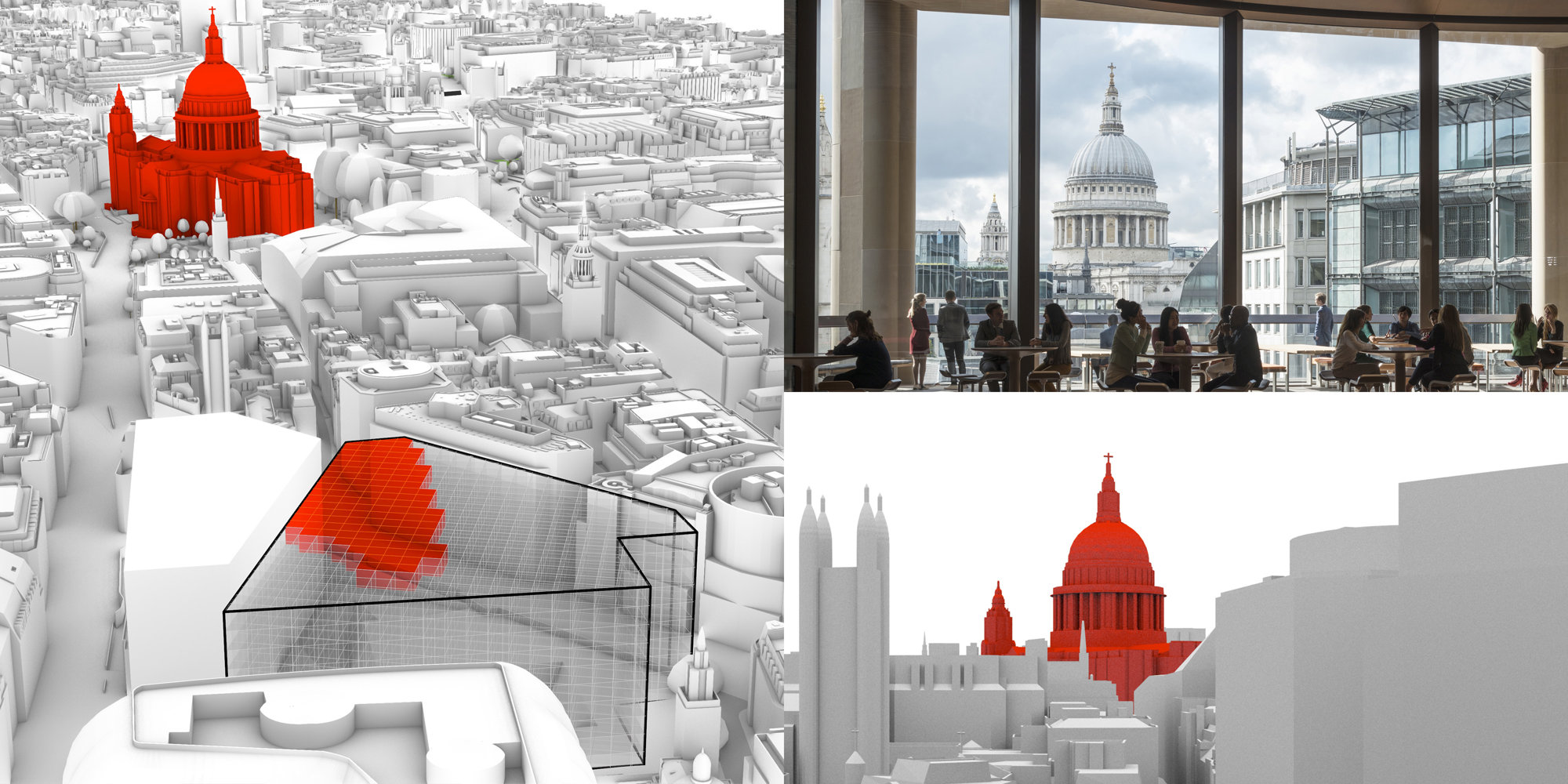
Bloomberg
Using our Quality of view analysis tools defining the best location and façade orientation of the pantry level at Bloomberg, giving the users of the pace uninterrupted views of the St. Paul’s Cathedral.
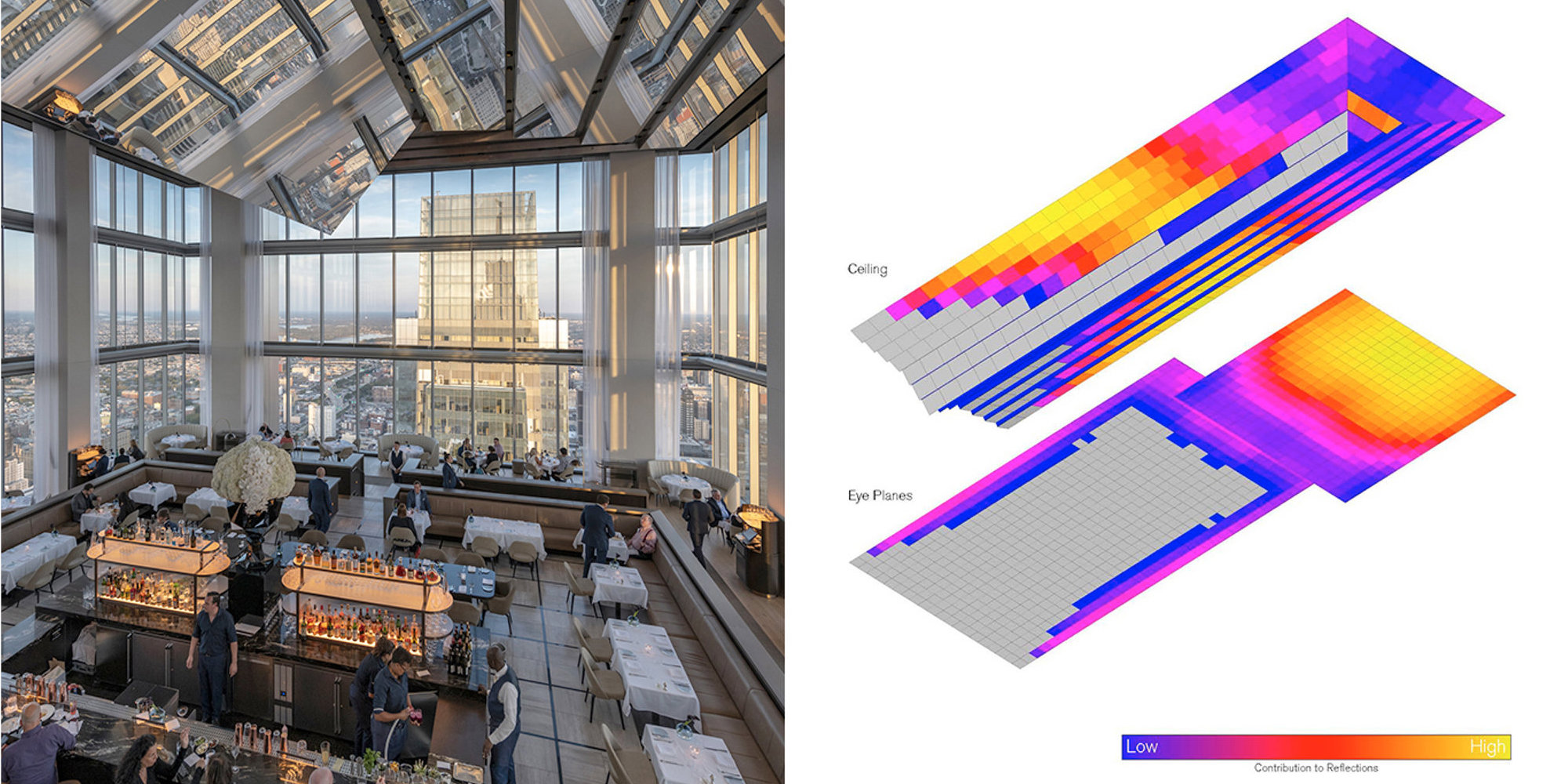
Comcast Technology Center, Sky High Lounge
The idea was to create a reflective ceiling for this triple-height space at the top of the tower, offering excellent views across the city to visitors. The Applied R+D team provided tools for exploring options in both virtual and augmented reality and evaluated options using bespoke software for analysing reflective potential from the horizon to the ceiling to the occupants.
Hydra
Hydra is a bespoke tool which takes large geometry generation and simulation tasks and splits them into smaller components which are automatically executed in parallel. Hydra allows to speed up the evolution process and analyse highly complex problems in hours and days instead of months. It allows us to create several thousand options at the early design stages.
Collaborative Design Tools
At Foster + Partners design is inherently collaborative. We are a multi-disciplinary, integrated design practice and accordingly we benefit from every opportunity to improve communication and the flow of information. The Applied R+D team develops tools and systems to help with design collaboration. These innovations include immersive, multi-use Extended Reality design systems and real-time design data exchange solutions. The team has also created innovative systems for transforming physical models and hand drawings into corresponding digital models and drawings that can be analysed and further manipulated in our design software.
Hermes
Hermes is a system developed by Foster + Partners for exchanging design data in real time between different software applications, computers, design disciplines and locations around the world. Hermes is a web application with client plugins for our CAD, BIM, interactive and business applications allowing for seamless collaboration. This facilitates our multi-disciplinary, integrated approach to design, improving coordination and accelerating design and analysis.
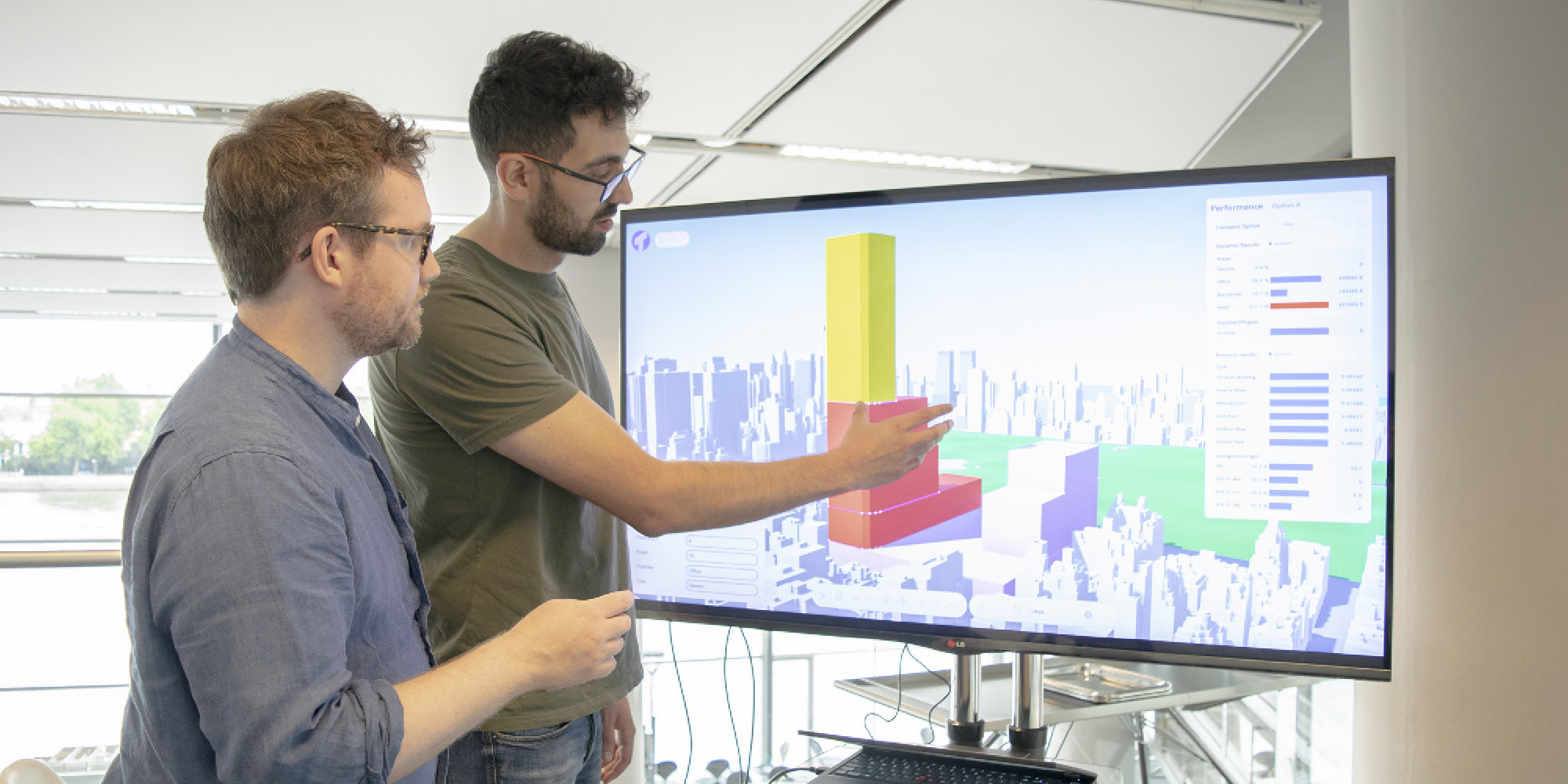
Thalia
Thalia is our latest performance-driven design system, allowing people to design, evaluate and compare ideas through a single intuitive interface. Thalia offers a multitude of metrics powered by our bespoke analysis tools. Designers can test their models against any and all of these in seconds.
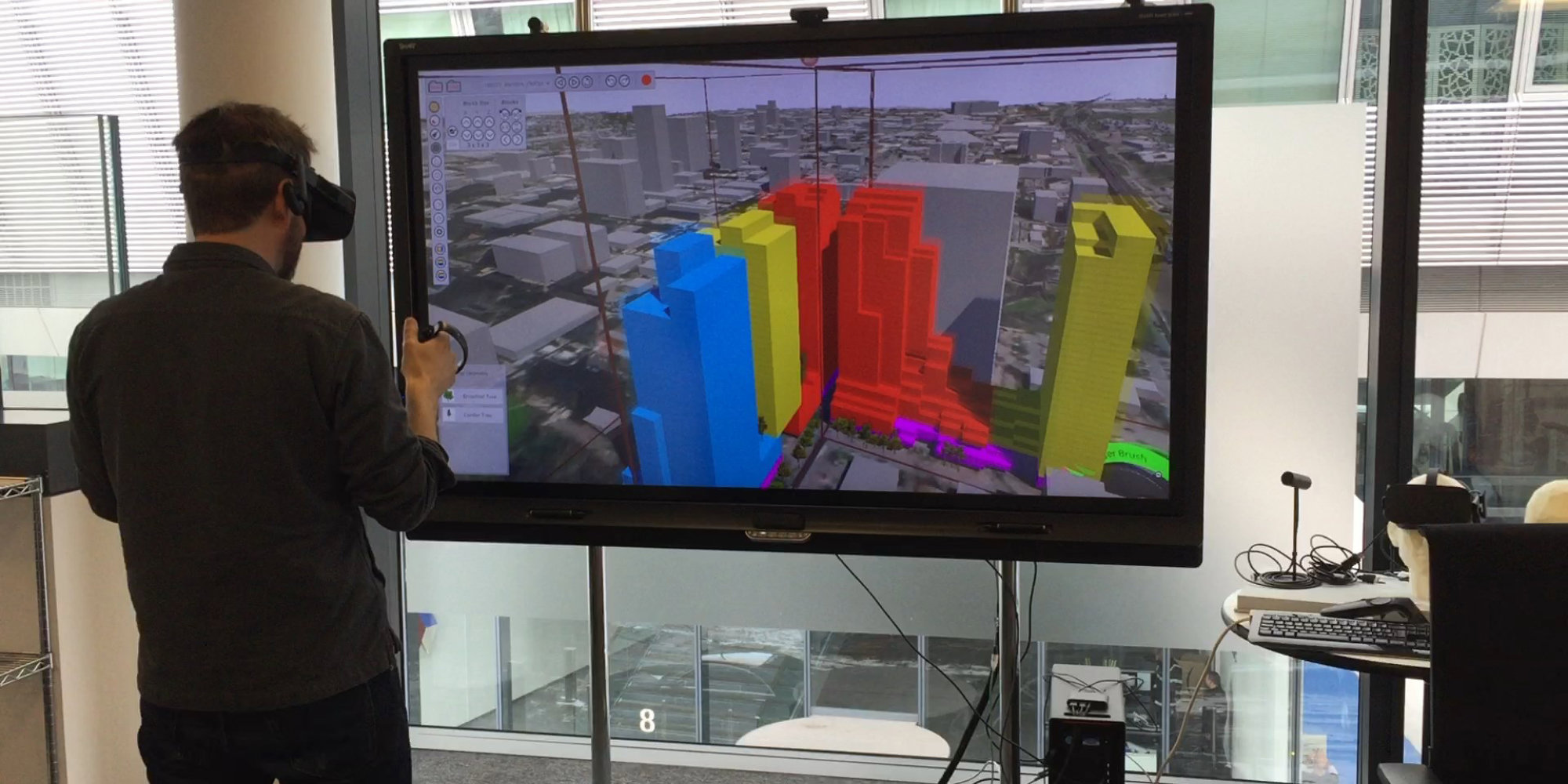
Sandbox
Sandbox is the latest generation of interactive design tools developed by the Applied R+D team. It takes advantage of recently developed games engines and is designed to be easy to set up and use in practice by designers. It is integrated in the design process at different scales from interiors and floorplates, through buildings, to masterplans.
Interoperability
Interoperability describes the use of multiple discrete technologies to create a cohesive digital artefact or workflow. At Foster + Partners our multi-disciplinary integrated design approach demands this tight integration from conception to completion. The Applied R+D team has developed bespoke software such as Hermes; which allow our designers, artists and stakeholders to collaborate on the same scene while working independently on their software of choice. Multiple design changes can be visualised simultaneously in real-time, allowing design options to be reviewed in parallel for faster design cycles.
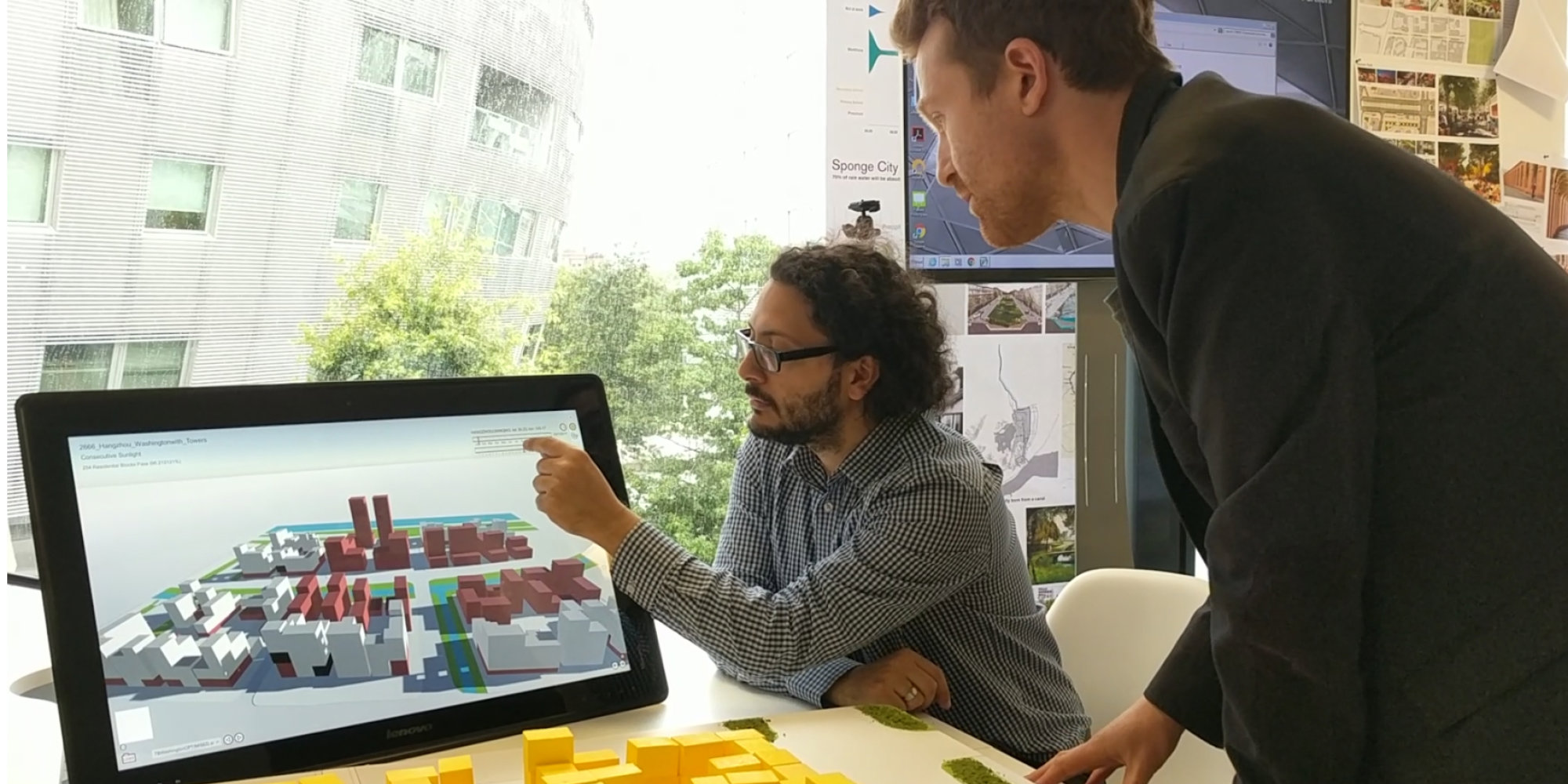
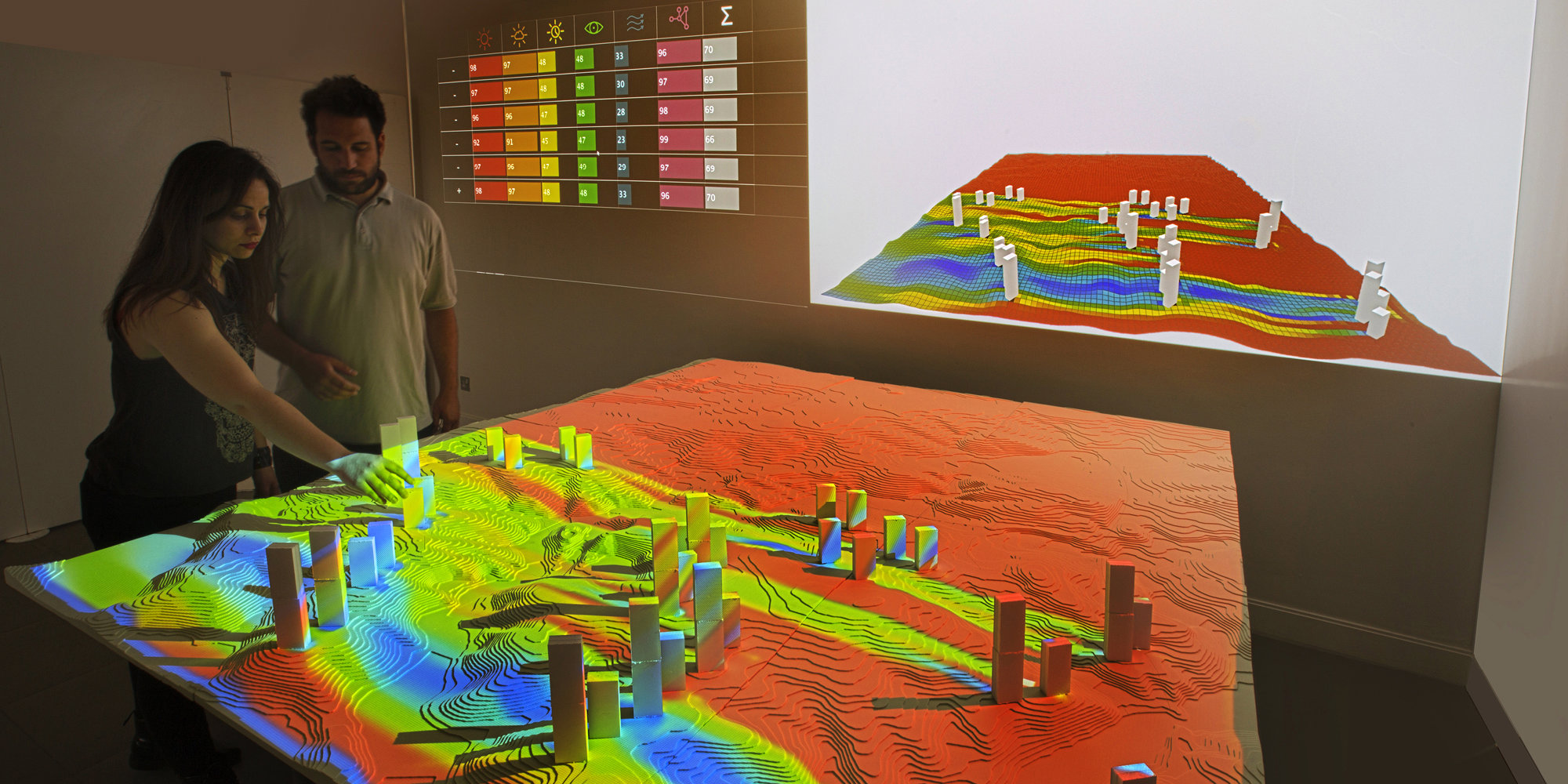
Interactive Physical Modelling
The IPM system is designed to break down the barriers between physical and digital modelling. By tracking a physical model as it is manipulated in real time, key metrics can be calculated on a linked digital model, allowing intuitive yet informed decision making, and the capture of design options as they evolve.
Interactive Modelling Environment
The bespoke IME is an application developed in collaboration with the Urban Design team which provides a tangible interface that allows the real time design development and analysis of urban schemes. The analyses include CFD, Insolation, Vertical Sky Component, Pedestrian Simulation and Isovists.
Experience and Interaction
Technologies such as virtual and augmented reality change the way we design and experience space, which extends beyond the physical into hybrid spatial environments. For over 20 years, we have been innovating at the cutting edge of these technologies. This includes developing tools that allow us to engage with the design process by creating augmented and virtual experiences that would otherwise be impossible through other means; whilst saving time, money and reducing our environmental impact.
Glaucon XR | Applied R+D
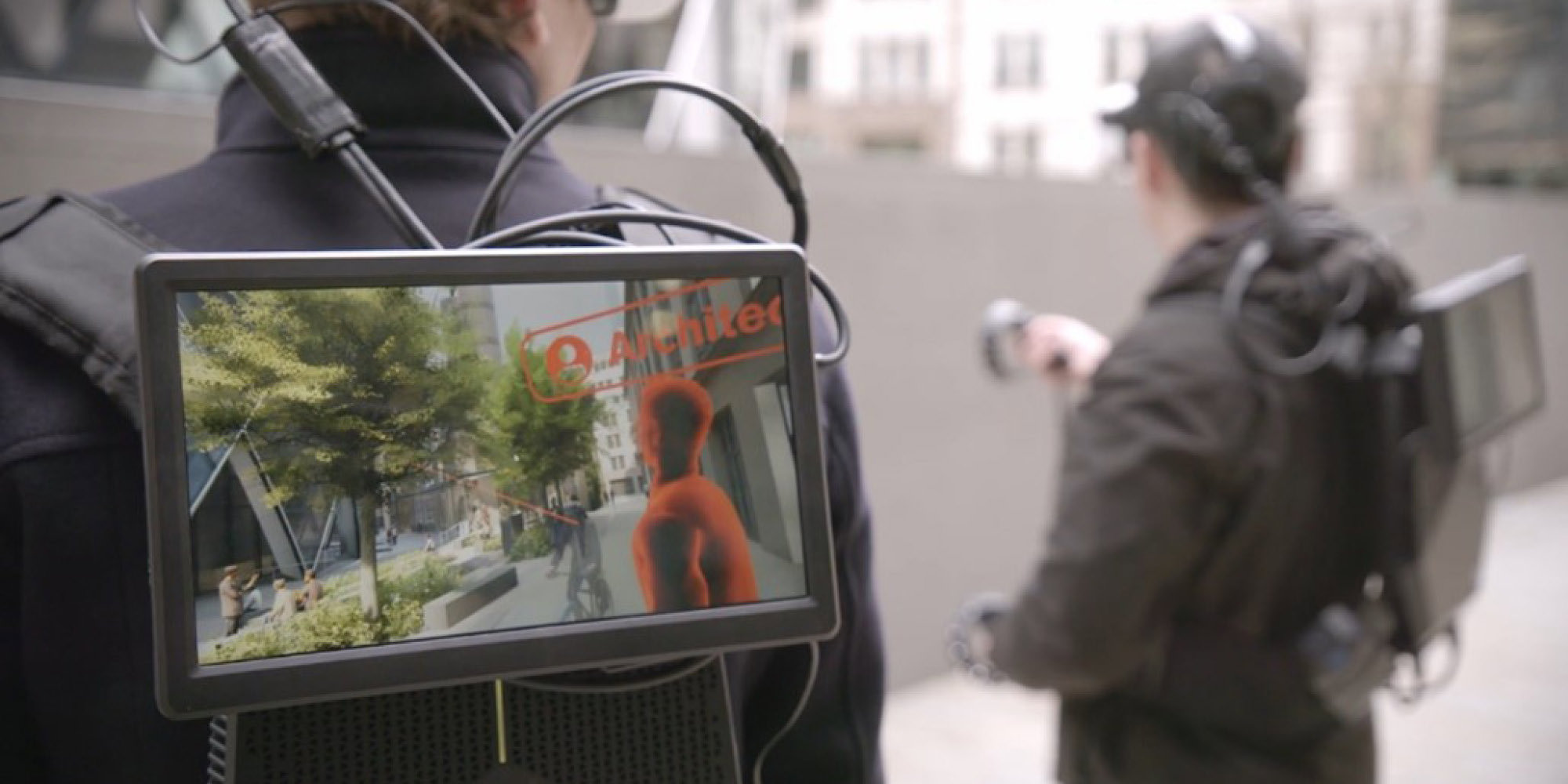
Glaucon XR
Glaucon has been used to extend a physical mock-up virtually using a VR backpack PC and VR headset. The ability to align physical and virtual experiences has enabled Glaucon to be used to augment and extend the physical environment at scale to experience projects as if they had been built in-situ. It has been used to increase accessibility and application reach and to allow users who may not have access to or be comfortable using head-mounted XR hardware.
Digital Design Review, Glaucon | Applied R+D
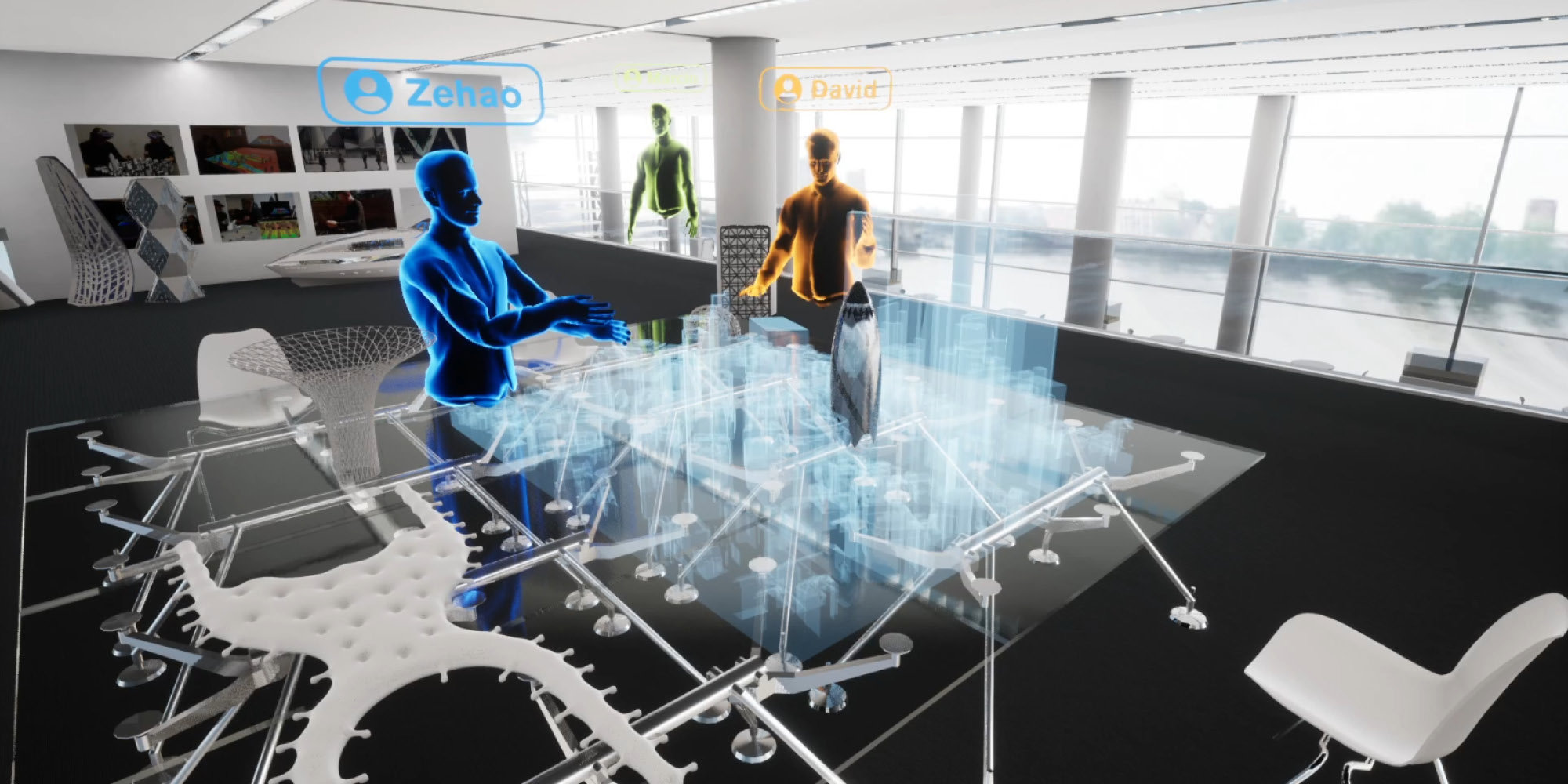
Digital Design Review, Glaucon
Glaucon provides an entirely virtual context, where users seek to experience or review an environment as if it were real. Multiple stakeholders could remotely engage virtually with the design and be part of the decision-making process. By combining the experience of the space with the detailed design models and enabling multi-user virtual collaboration, the impact of the design could be effectively understood. Several environments have also been collaboratively developed to create the basis for a formalised review environment, allowing live project content to be loaded, cycled, reviewed and saved for immediate recall at a later point.
Sandbox VR | Applied R+D
Sandbox VR
Sandbox VR integration combined the power of the sandbox tool with a set of intuitive gestures specific for head-mounted displays. Using the controllers, users can scale themselves by grabbing a digital model and pushing or pulling their hands apart or together. These techniques proved highly intuitive and effective and had the added benefit of almost completely avoiding user motion sickness, which can be a common occurrence with other VR navigation techniques.
Digital Twins, Smart Buildings and Internet of Things
As Extended Reality provides us with sensory experience of space, digital twin technology provides us with data about the world around us. A Digital Twin is a computer model of a thing or process in the real world. Our Applied R+D team is building bespoke cloud systems for managing and visualising Digital Twins and Smart Buildings. We use the knowledge gained from this research and development to help our clients develop smart buildings that combine the best design and the best technology for an integrated experience that is more than the sum of its parts.
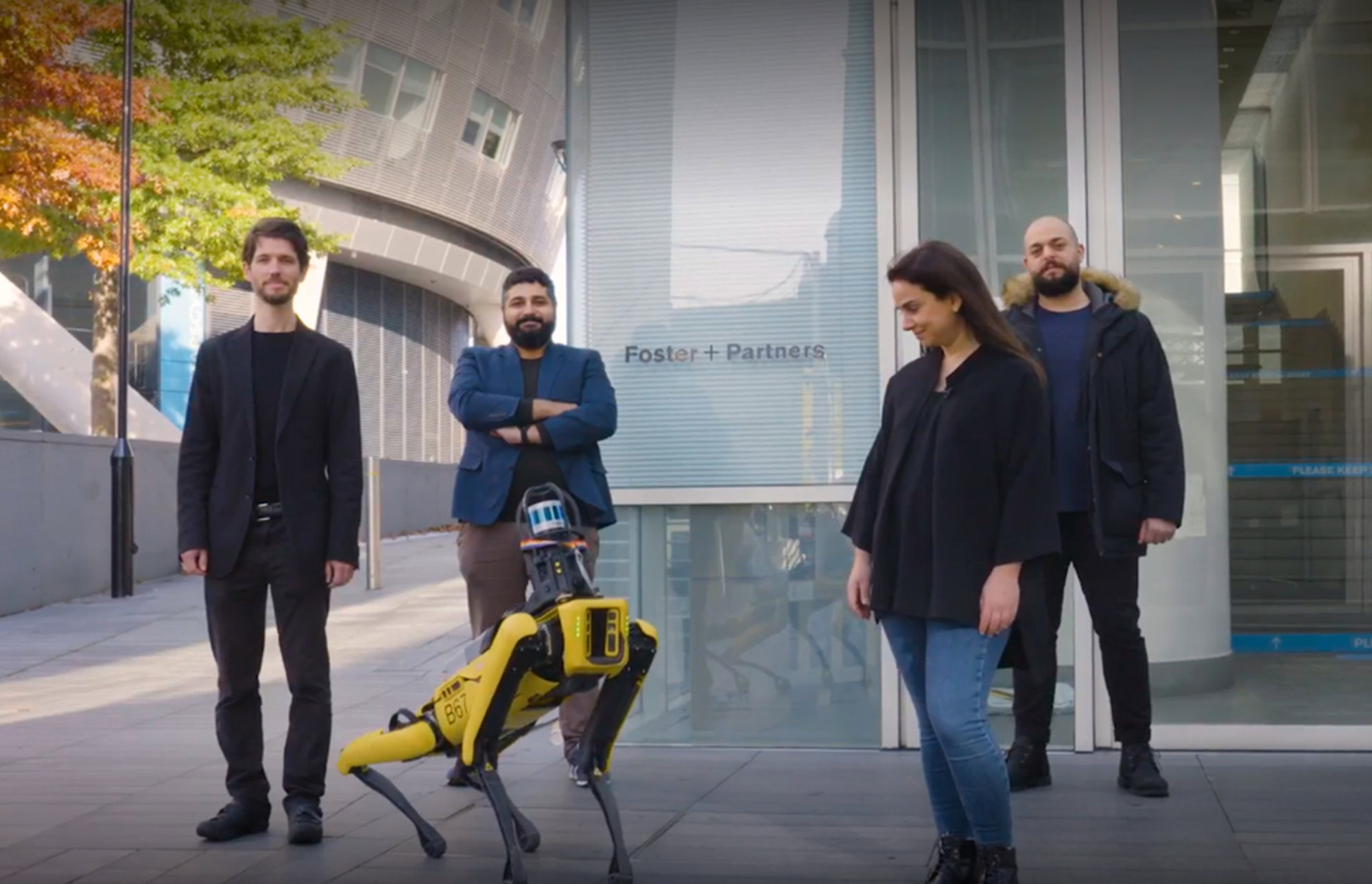
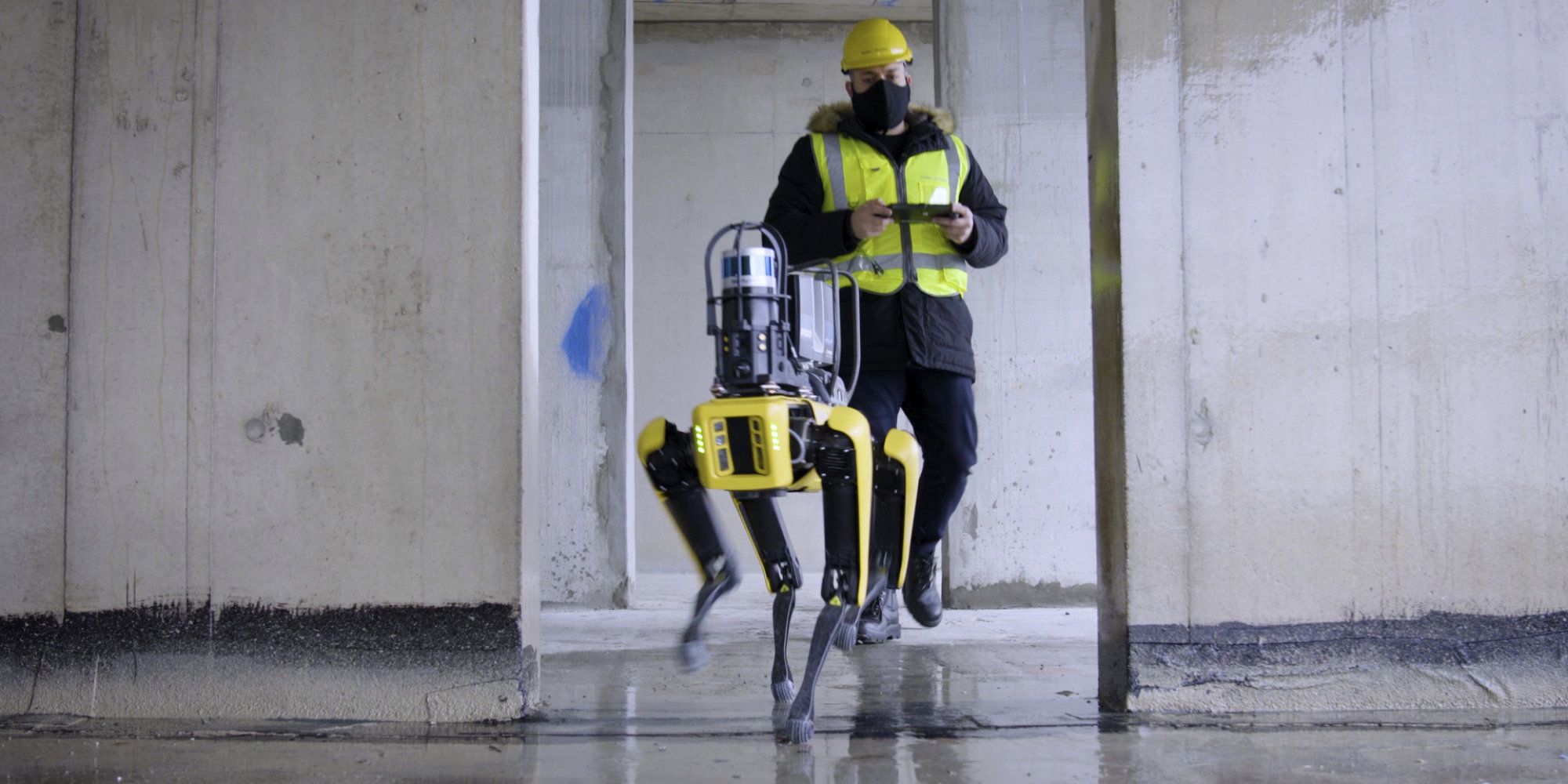
Spot
Foster + Partners was the first architecture practice to participate in Boston Dynamics' Early Adopters program for Spot, the semi-autonomous robot, to investigate how cutting-edge technologies can push the boundaries of both design and construction. Using 3D laser scanners mounted on Spot, we are capturing and monitoring construction progress on building sites, as well as changes to furniture layouts in completed buildings.
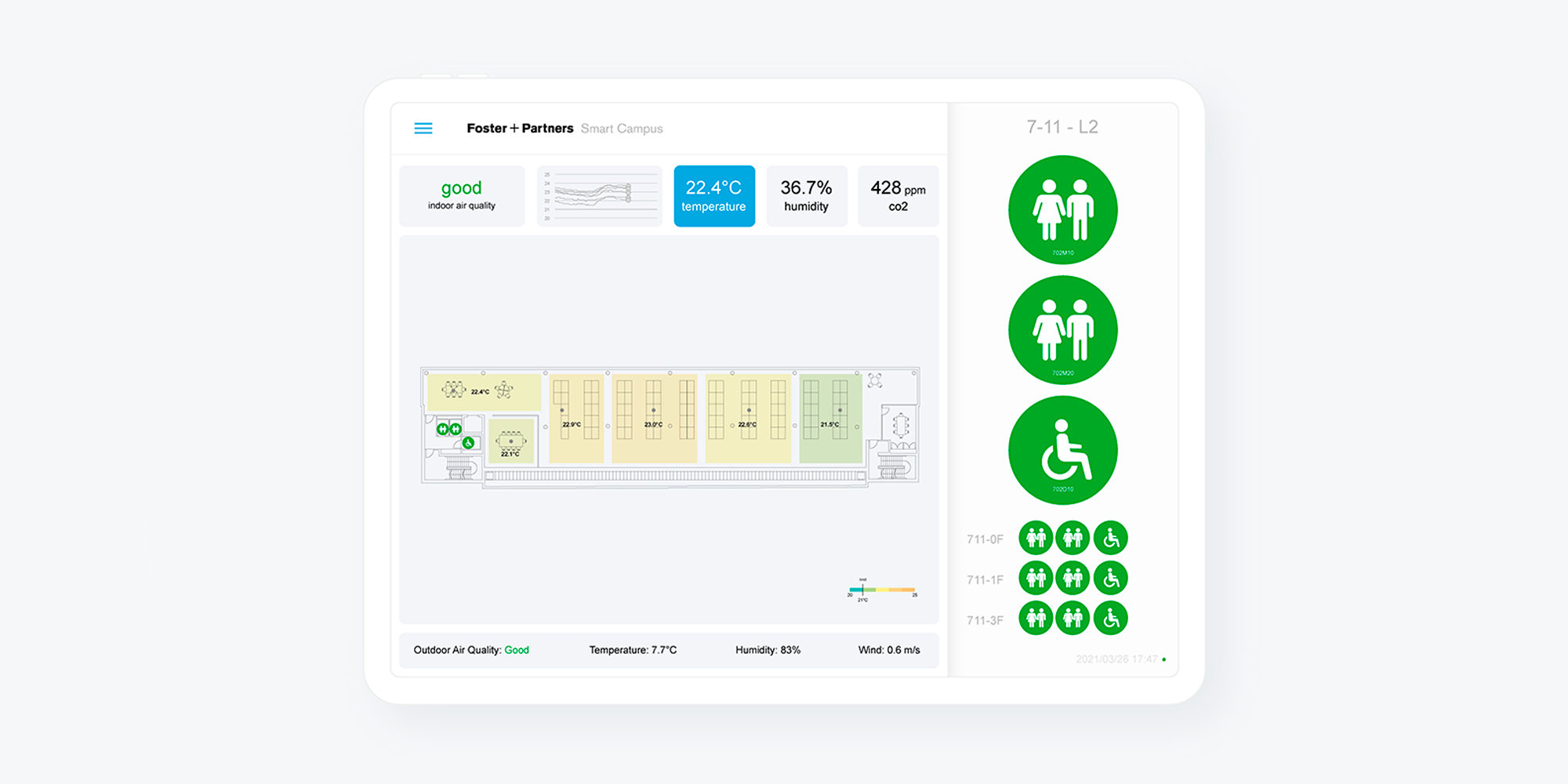
Smart Campus
The Smart Campus uses smart building technology to gain insight about patterns of visitation, environment, and energy usage. Sensors are installed to monitor temperature, humidity, CO2 and washroom occupancy. An external sensor monitors climate and air quality. The dashboard provides a view of the various data. It can be used to see patterns over the course of a day, as well as during a specific 15-minute interval.
Digital Twin
The Applied R+D team have been conducting research into Post-Occupancy Digital Twins, which are focusing on how a physical space is being used. Here, spatial snapshots are used in combination with other data sources, such as occupancy levels and environmental information which combine to form a digital model of the existing which can engage with other digital tools and services.
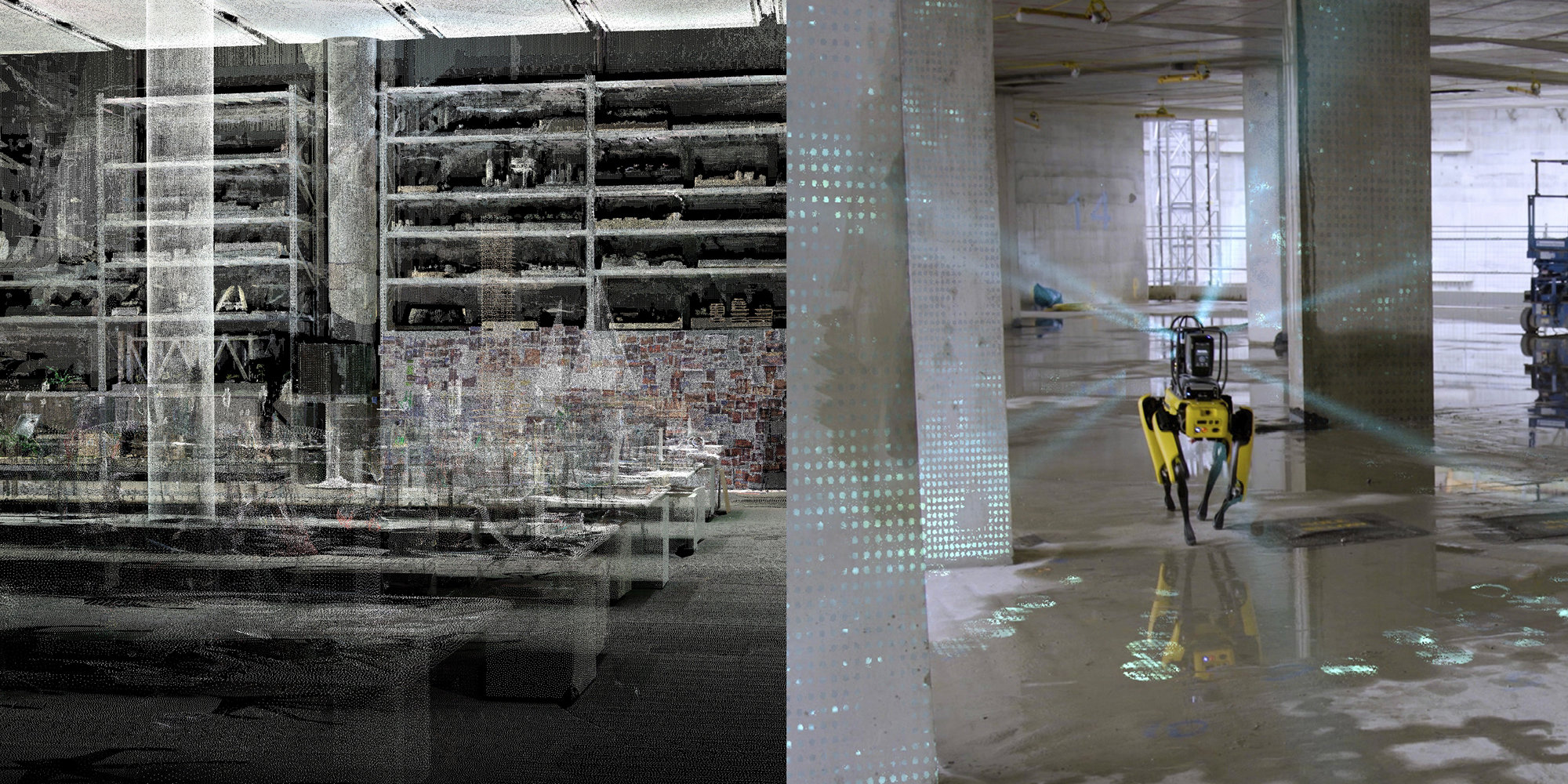
Reality Capture
Construction sites are inherently dynamic environments, where changes need to be tracked and measured on a regular basis, capturing errors in time to meet the project timeframe and budget. The Applied R+D team have been hands-on with reality capture technologies, such as laser scanning, SLAM-based lidar scanning and photogrammetry.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
In the past five years we have seen huge advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, resurrecting the interest on these technologies and the effect they can have in the way we work. The Applied R+D team is embracing Machine Learning to enhance our knowledge, instincts and sensitivities, free us from routine tasks, and to optimise and push the boundaries of design.
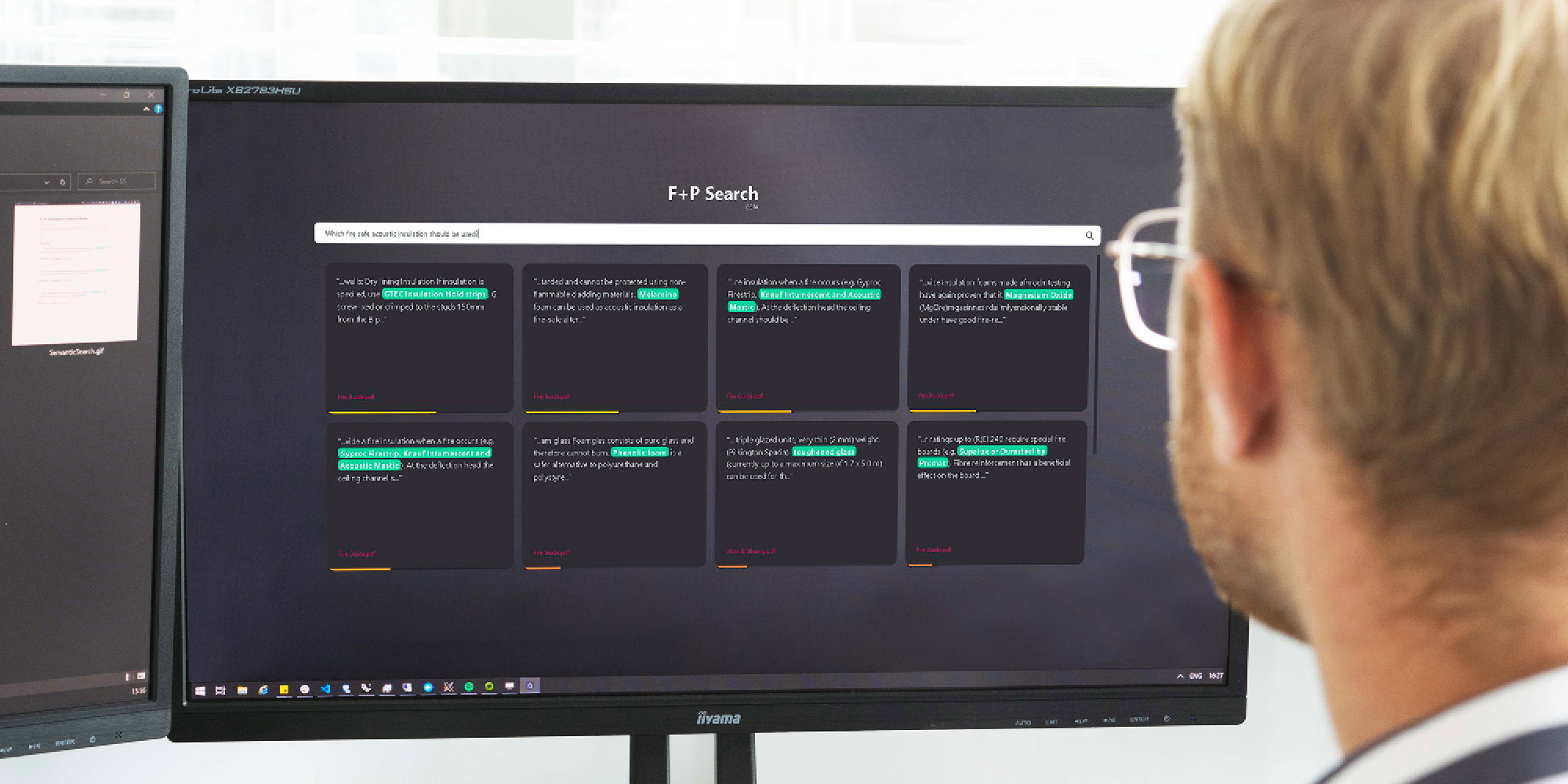
Natural Language Design Assist
We utilise Machine Learning techniques to help us sift through current and historical data. Adding a layer of semantic understanding on top of this data using natural language processing (NLP). Foster + Partners’ search application is a demonstration of the potential of such technology and allowing designers to find answers to pressing questions in the design guidelines.
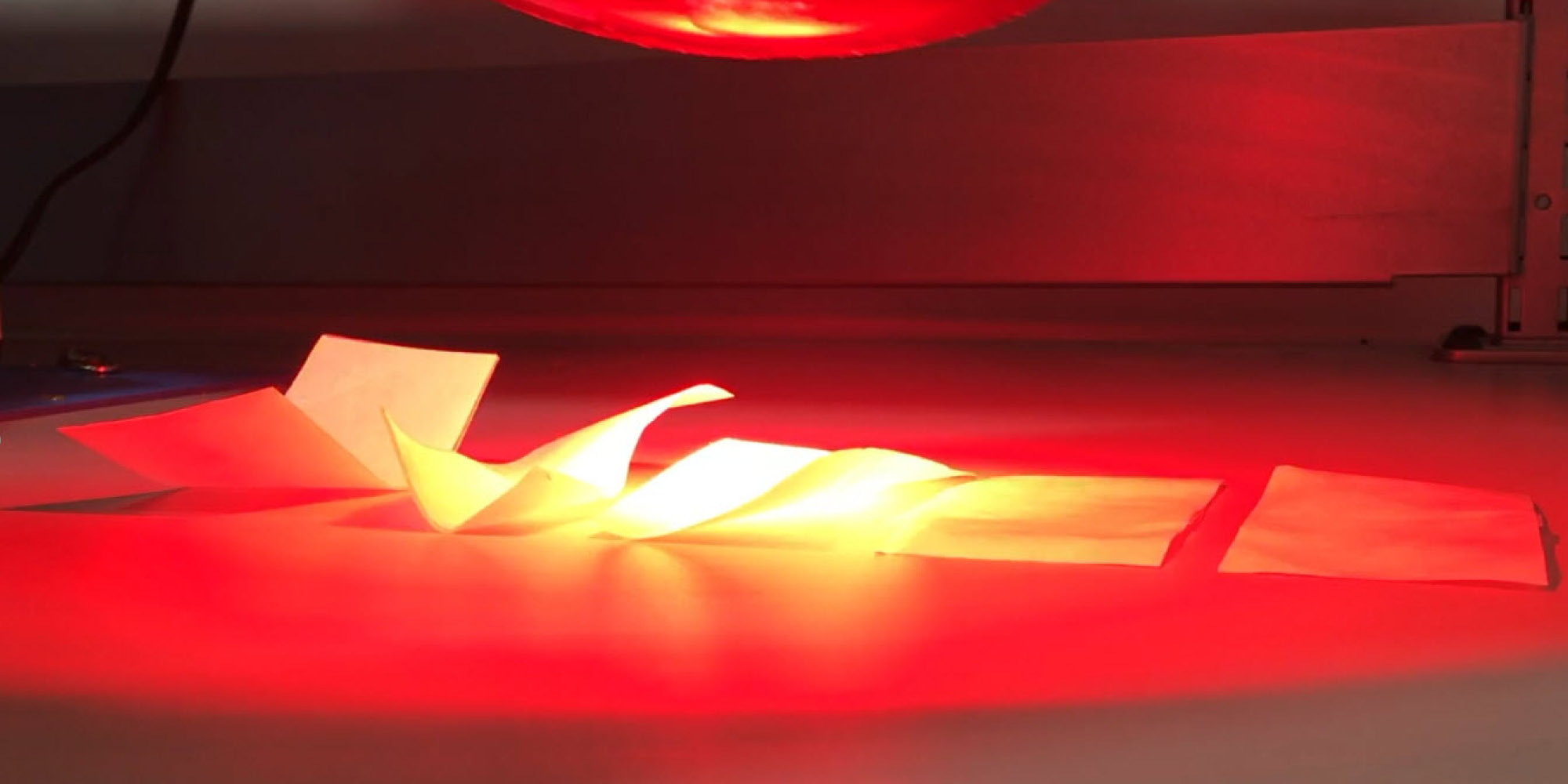
Passively Actuated Laminates
In collaboration with Autodesk, we used artificial intelligence to predict how a passively actuated material would react to temperature. With the help of Hydra we ran thousands of simulations to understand how thermo-active laminated behave under varied heat conditions. We then used that data to train a deep neural network to tell us what the laminate layering should be given a particular deformation we required.
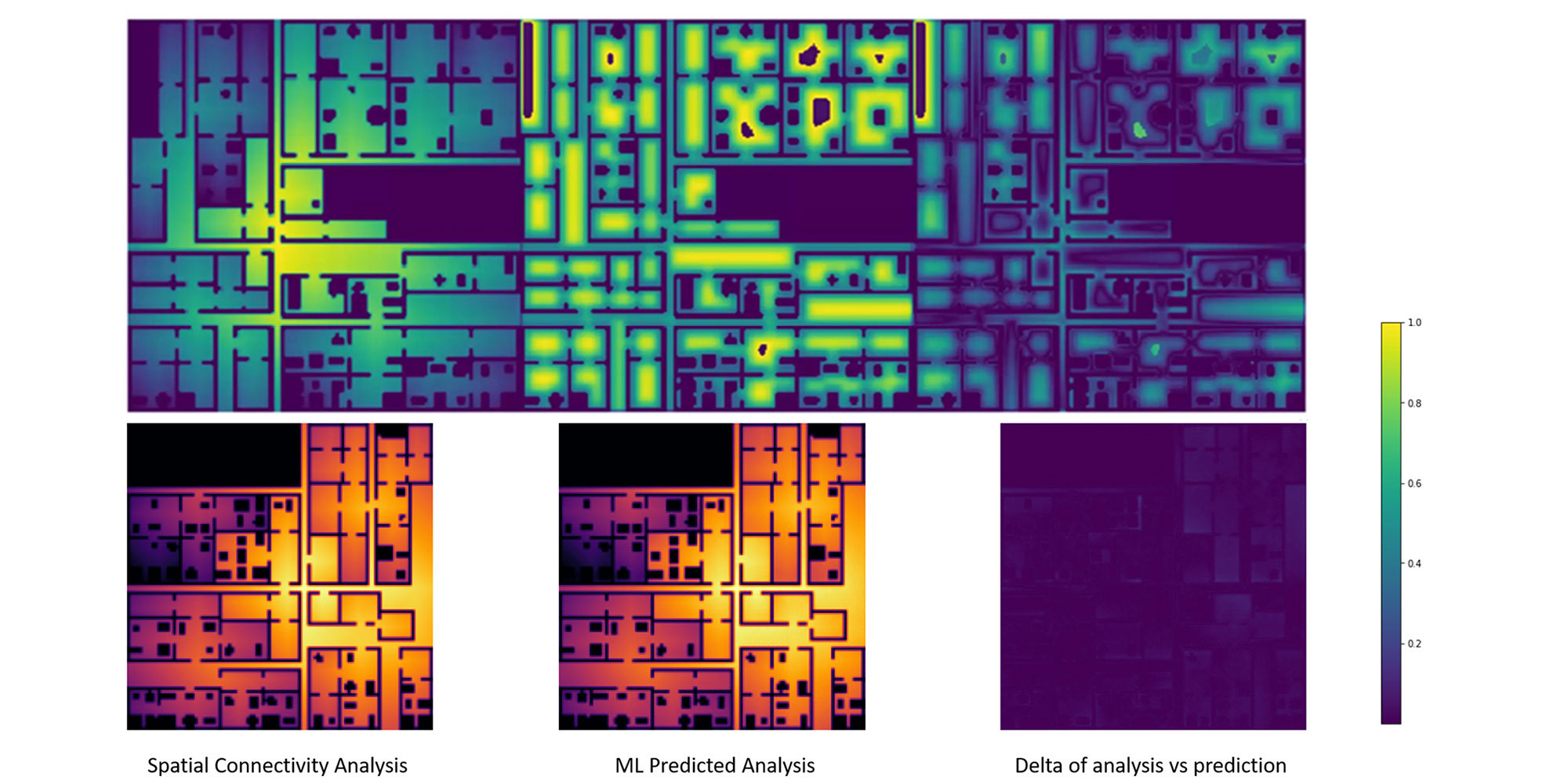
Spatial and Visual Connectivity
We used machine learning to teach a tool to approximate the complex analysis of visual and spatial connectivity, by training it with a generative dataset of tens of thousands of actual analysis. The predicted output is extremely comparable to the actual analysis and takes around 0.03 seconds to calculate, οffering vastly improved speeds.